Derlin-1 facilitates the retro-translocation of cholera toxin
- PMID: 18094046
- PMCID: PMC2262961
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-08-0755
Derlin-1 facilitates the retro-translocation of cholera toxin
Abstract
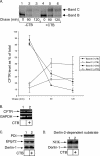
Cholera toxin (CT) intoxicates cells by using its receptor-binding B subunit (CTB) to traffic from the plasma membrane to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In this compartment, the catalytic A1 subunit (CTA1) is unfolded by protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and retro-translocated to the cytosol where it triggers a signaling cascade, leading to secretory diarrhea. How CT is targeted to the site of retro-translocation in the ER membrane to initiate translocation is unclear. Using a semipermeabilized-cell retro-translocation assay, we demonstrate that a dominant-negative Derlin-1-YFP fusion protein attenuates the ER-to-cytosol transport of CTA1. Derlin-1 interacts with CTB and the ER chaperone PDI as assessed by coimmunoprecipitation experiments. An in vitro membrane-binding assay showed that CTB stimulated the unfolded CTA1 chain to bind to the ER membrane. Moreover, intoxication of intact cells with CTB stabilized the degradation of a Derlin-1-dependent substrate, suggesting that CT uses the Derlin-1 pathway. These findings indicate that Derlin-1 facilitates the retro-translocation of CT. CTB may play a role in this process by targeting the holotoxin to Derlin-1, enabling the Derlin-1-bound PDI to unfold the A1 subunit and prepare it for transport.
Figures




References
-
- Carvalho P., Goder V., Rapoport T. A. Distinct ubiquitin-ligase complexes define convergent pathways for the degradation of ER proteins. Cell. 2006;126:361–373. - PubMed
-
- Denic V., Quan E. M., Weissman J. S. A luminal surveillance complex that selects misfolded glycoproteins for ER-associated degradation. Cell. 2006;126:349–359. - PubMed
-
- Fujinaga Y., Wolf A. A., Rodighiero C., Wheeler H., Tsai B., Allen L., Jobling M. G., Rapoport T., Holmes R. K., Lencer W. I. Gangliosides that associate with lipid rafts mediate transport of cholera and related toxins from the plasma membrane to endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2003;14:4783–4793. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gauss R., Jarosch E., Sommer T., Hirsch C. A complex of Yos9p and the HRD ligase integrates endoplasmic reticulum quality control into the degradation machinery. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006;8:849–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

