A novel site of action for alpha-SNAP in the SNARE conformational cycle controlling membrane fusion
- PMID: 18094056
- PMCID: PMC2262999
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0498
A novel site of action for alpha-SNAP in the SNARE conformational cycle controlling membrane fusion
Abstract
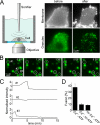
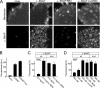
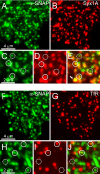
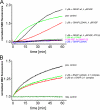
Regulated exocytosis in neurons and neuroendocrine cells requires the formation of a stable soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complex consisting of synaptobrevin-2/vesicle-associated membrane protein 2, synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa (SNAP-25), and syntaxin 1. This complex is subsequently disassembled by the concerted action of alpha-SNAP and the ATPases associated with different cellular activities-ATPase N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF). We report that NSF inhibition causes accumulation of alpha-SNAP in clusters on plasma membranes. Clustering is mediated by the binding of alpha-SNAP to uncomplexed syntaxin, because cleavage of syntaxin with botulinum neurotoxin C1 or competition by using antibodies against syntaxin SNARE motif abolishes clustering. Binding of alpha-SNAP potently inhibits Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis of secretory granules and SNARE-mediated liposome fusion. Membrane clustering and inhibition of both exocytosis and liposome fusion are counteracted by NSF but not when an alpha-SNAP mutant defective in NSF activation is used. We conclude that alpha-SNAP inhibits exocytosis by binding to the syntaxin SNARE motif and in turn prevents SNARE assembly, revealing an unexpected site of action for alpha-SNAP in the SNARE cycle that drives exocytotic membrane fusion.
Figures



References
-
- Banerjee A., Barry V. A., DasGupta B. R., Martin T. F. N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor acts at a prefusion ATP-dependent step in Ca2+-activated exocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:20223–20226. - PubMed
-
- Barnstable C. J., Hofstein R., Akagawa K. A marker of early amacrine cell development in rat retina. Brain Res. 1985;352:286–290. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

