Binding of ICP4, TATA-binding protein, and RNA polymerase II to herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early, early, and late promoters in virus-infected cells
- PMID: 18094162
- PMCID: PMC2258917
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02459-07
Binding of ICP4, TATA-binding protein, and RNA polymerase II to herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early, early, and late promoters in virus-infected cells
Abstract
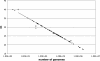
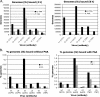
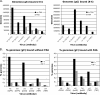
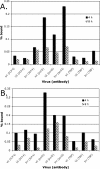
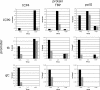
The binding of herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4, TATA-binding protein (TBP), and RNA polymerase II (polII) to the promoter regions of representative immediate-early (IE) (ICP0), early (E) (thymidine kinase [tk]), and late (L) (glycoprotein C [gC]) genes on the viral genome was examined as a function of time postinfection, viral DNA replication, cis-acting sites for TFIID in the tk and gC promoters, and genetic background of ICP4. The binding of TBP and polII to the IE ICP0 promoter was independent of the presence of ICP4, whereas the binding of TBP and polII to the tk and gC promoters occurred only when ICP4 also bound to the promoters, suggesting that the presence of ICP4 at the promoters of E and L genes in virus-infected cells is crucial for the formation of transcription complexes on these promoters. When the TATA box of the tk promoter or the initiator element (INR) of the gC promoter was mutated, a reduction in the amount of TBP and polII binding was observed. However, a reduction in the amount of ICP4 binding to the promoters was also observed, suggesting that the binding of TBP-containing complexes and ICP4 is cooperative. The binding of ICP4, TBP, and polII was also observed on the gC promoter at early times postinfection or when DNA synthesis was inhibited, suggesting that transcription complexes may be formed early on L promoters and that additional events or proteins are required for expression. The ability to form these early complexes on the gC promoter required the DNA-binding domain but in addition required the carboxyl-terminal 524 amino acids of ICP4, which is missing the virus n208. This region was not required to form TBP- and polII-containing complexes on the tk promoter. n208 activates E but not L genes during viral infection. These data suggest that a region of ICP4 may differentiate between forming TBP- and polII-containing complexes on E and L promoters.
Figures


References
-
- Alwine, J. C., W. L. Steinhart, and C. W. Hill. 1974. Transcription of herpes simplex type 1 DNA in nuclei isolated from infected HEp-2 and KB cells. Virology 60302-307. - PubMed
-
- Campbell, M. E., J. W. Palfreyman, and C. M. Preston. 1984. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J. Mol. Biol. 1801-19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

