Association of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 with coronary calcification among American and Japanese men
- PMID: 18094516
- PMCID: PMC3659786
- DOI: 10.2188/jea.17.179
Association of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 with coronary calcification among American and Japanese men
Abstract
Background: We have previously reported that the prevalence of coronary artery calcification (CAC) was substantially lower among Japanese than American men despite a less favorable profile of many traditional risk factors in Japanese men. To determine whether lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) levels are related to the difference in the prevalence of CAC between the two populations.
Methods: A total of 200 men aged 40-49 years were examined: 100 residents in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and 100 residents in Kusatsu City, Shiga, Japan. Coronary calcium score (CCS) was evaluated by electron-beam tomography, Lp-PLA2 levels, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) lipoprotein subclasses, and other factors were assessed in 2001-2002.
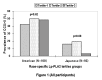
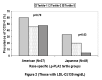
Results: Lp-PLA2 levels were higher among American than Japanese men (Mean +/- standard deviation 301.7 +/- 82.6 versus 275.9 +/- 104.7 ng/mL, respectively, p=0.06). Among all Japanese men and those with low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol > or =130 mg/dL, there was an inverse association of the prevalence of CCS>0 with the tertile groups of Lp-PLA2 levels (p=0.08 and p=0.03, respectively). American men did not have any association between CCS>0 with the tertile groups of Lp-PLA2 (p=0.62). Although Lp-PLA2 among both populations correlated positively with LDL and total cholesterol, American and Japanese men had different correlations with NMR lipoprotein subclasses. Reported high odds ratio for CCS>0 among American compared to Japanese men was not reduced after adjusting for Lp-PLA2 levels.
Conclusion: Lp-PLA2 may have different mechanisms of action among American and Japanese men. Lp-PLA2 levels can not explain the observed CAC differences between the two populations.
Figures
References
-
- Yamada Y, Ichihara S, Fujimura T, Yokota M.. Identification of the G994--> T missense in exon 9 of the plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase gene as an independent risk factor for coronary artery disease in Japanese men. Metabolism 1998; 47: 177-81. 10.1016/S0026-0495(98)90216-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yamada Y, Yoshida H, Ichihara S, Imaizumi T, Satoh K, Yokota M.. Correlations between plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) activity and PAF-AH genotype, age, and atherosclerosis in a Japanese population. Atherosclerosis 2000; 150: 209-16. 10.1016/S0021-9150(99)00385-8 - DOI - PubMed

