Lombard's effect's implication in intensity, fundamental frequency and stability on the voice of individuals with Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 18094810
- PMCID: PMC9445896
- DOI: 10.1016/s1808-8694(15)30129-4
Lombard's effect's implication in intensity, fundamental frequency and stability on the voice of individuals with Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Parkinson's disease affects the central nervous system resulting in voice quality alterations. It is typically resistant to drug therapy and often persists despite extensive behavioural speech and language therapy. Previous findings show that masking noise will produce a consistent increase in voice intensity in most normal individuals (Lombard's effect).
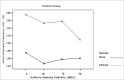
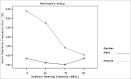
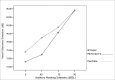
Aim: we evaluated Lombard's effect's implication in intensity, fundamental frequency and stability on the voice of individuals with Parkinson's disease (N=17).
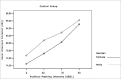
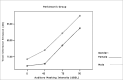
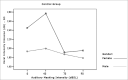
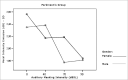
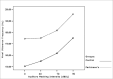
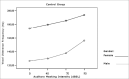
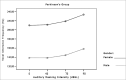
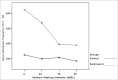
Material and methods: through acoustic analysis, we evaluated intensity alterations and fundamental frequency, before and after white masking noise 40, 70 and 90 dBSL intensities, as well as variations during each vocalization and compared with a control group (N=16).
Results: voice intensity varied according to masking intensity, tending to non-linear increases in both groups and gender. Fundamental frequency varied, tending to non-linear increase in both groups and gender. Improvement stability occurred in fundamental frequency and vocal intensity.
Conclusion: Lombard's effect increased intensity, fundamental frequency and improves voice stability on these patients.
Study: clinical and experimental.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Assessment of vocal intensity in lecturers depending on acoustic properties of lecture rooms].Med Pr. 2015;66(4):487-96. doi: 10.13075/mp.5893.00180. Med Pr. 2015. PMID: 26536966 Polish.
-
Relationship Between Voice and Motor Disabilities of Parkinson's Disease.J Voice. 2016 Nov;30(6):768.e17-768.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2015.10.022. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Voice. 2016. PMID: 26725551
-
Voice and speech of individuals with Parkinson s Disease during amplification, delay and masking situations.Pro Fono. 2009 Jul-Sep;21(3):219-24. doi: 10.1590/s0104-56872009000300007. Pro Fono. 2009. PMID: 19838568
-
Acoustic analysis of voice in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review of voice disability and meta-analysis of studies.Rev Neurol. 2020 Jun 1;70(11):393-405. doi: 10.33588/rn.7011.2019414. Rev Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32436206 English, Spanish.
-
[Speech and voice disorders in Parkinson's disease].Rev Neurol. 2010 Nov 1;51(9):542-50. Rev Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20979034 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Laryngeal Aerodynamics in Healthy Older Adults and Adults With Parkinson's Disease.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017 Mar 1;60(3):507-524. doi: 10.1044/2016_JSLHR-S-14-0314. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017. PMID: 28241225 Free PMC article.
-
Speech and language therapy versus placebo or no intervention for speech problems in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;2012(8):CD002812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002812.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22895930 Free PMC article.
-
Vocal responses to perturbations in voice auditory feedback in individuals with Parkinson's disease.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033629. Epub 2012 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22448258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Mattos JP. In: Doença de Parkinson. Aspectos clínicos e cirúrgicos. 2nd. Meneses MS, Teive HAG, editors. Guanabara Koogan; Rio de Janeiro: 1996. Diagnóstico diferencial.
-
- Logemann JA, Fisher HB, Boshes B, Blonsky ER, et al. Frequency and occurrence of vocal tract dysfunctions in the speech of a large sample of Parkinson patients. J Speech Hear Disord. 1978;43(1):47–57. - PubMed
-
- Streifler M, Hofman S. Disorders of verbal expression in parkinsonism. Adv Neurol. 1984;40:385–393. - PubMed
-
- Illes J, Metter EJ, Hanson WR, Iritani S. Language production in Parkinsons disease: acoustic and linguistic considerations. Brain Lang. 1988;33(1):146–160. - PubMed
-
- Holmes RJ, Oates JM, Phyland DJ, Hughes AJ. Voice characteristics in the progression of Parkinsons disease. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2000;35(3):407–418. - PubMed
Uncited Reference
-
- Isshiki N, Okamura H, Tanabe M, Morimoto M. Differential diagnosis of hoarseness. Folia Phoniatr (Basel) 1969;21(1):9–19. - PubMed
-
- Webster DD. Critical analysis of the disability in Parkinson’s disease. Mod Treat. 1968;5:257–282. - PubMed
-
- Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonism: onset, progression, and mortality. Neurology. 1967;17:427–442. - PubMed
-
- Behlau M. Voz. O livro do especialista. Revinter; São Paulo: 2001. pp. 130–163.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

