The antidepressant sertraline improves the phenotype, promotes neurogenesis and increases BDNF levels in the R6/2 Huntington's disease mouse model
- PMID: 18096160
- PMCID: PMC2278120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.10.015
The antidepressant sertraline improves the phenotype, promotes neurogenesis and increases BDNF levels in the R6/2 Huntington's disease mouse model
Abstract
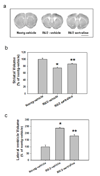
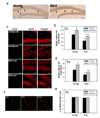
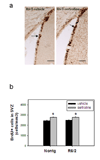
Huntington's disease (HD) is an inherited progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive movement, psychiatric and cognitive disturbances. Previous studies have indicated that HD pathogenesis may be mediated in part by loss of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Antidepressants selectively blocking serotonin reuptake can increase BDNF levels, and also may increase neurogenesis. Here we report that an SSRI antidepressant, sertraline, prolongs survival, improves motor performance, and ameliorates brain atrophy in the R6/2 HD mouse model. Six-week-old R6/2 mice and nontransgenic control mice were administered either sertraline or vehicle daily. Motor function was assessed in an accelerating rotarod test and evaluated at 10 weeks. R6/2 mice exhibited reduced time on the rod. Sertraline treatment improved the motor performance in R6/2 mice, but did not affect nontransgenic mice. R6/2 mice showed significant striatal atrophy which was reduced by sertraline treatment. These beneficial effects of sertraline are associated with enhanced neurogenesis and increased BDNF levels in brain treated with sertraline. The effective serum and brain levels of sertraline are comparable to the levels achieved in human antidepressant treatment. Our findings provide evidence that sertraline is neuroprotective in this HD model. Successful treatment with sertraline in depressed HD patients has been reported; moreover, sertraline is safe and well-tolerated for long-term administration, including in HD patients. Our findings suggest that a clinical trial of SSRI treatment in order to retard disease progression in human HD may be warranted.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sertraline slows disease progression and increases neurogenesis in N171-82Q mouse model of Huntington's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2008 Jun;30(3):312-322. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.01.015. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2008. PMID: 18403212 Free PMC article.
-
A small molecule TrkB ligand reduces motor impairment and neuropathology in R6/2 and BACHD mouse models of Huntington's disease.J Neurosci. 2013 Nov 27;33(48):18712-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1310-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24285878 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between BDNF expression in major striatal afferents, striatum morphology and motor behavior in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington's disease.Genes Brain Behav. 2013 Feb;12(1):108-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00858.x. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Genes Brain Behav. 2013. PMID: 23006318
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Huntington's Disease: Neurobiology and Therapeutic Potential.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025;23(4):384-403. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22666240530105516. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40123457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington's disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2007 Apr;81(5-6):294-330. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Feb 9. Prog Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17379385 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered dopamine and serotonin metabolism in motorically asymptomatic R6/2 mice.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 31;6(3):e18336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018336. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21483838 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation increases the development of depression behaviors in male rats after spinal cord injury.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021 Apr 19;14:100258. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100258. eCollection 2021 Jul. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021. PMID: 34589764 Free PMC article.
-
Adult neurogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Apr 1;7(4):a021287. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021287. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25833845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The α crystallin domain of small heat shock protein b8 (Hspb8) acts as survival and differentiation factor in adult hippocampal neurogenesis.J Neurosci. 2013 Mar 27;33(13):5785-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6452-11.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23536091 Free PMC article.
-
Rosmarinic acid ameliorates depressive-like behaviors in a rat model of CUS and Up-regulates BDNF levels in the hippocampus and hippocampal-derived astrocytes.Neurochem Res. 2013 Sep;38(9):1828-37. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1088-y. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23756732
References
-
- Bemelmans AP, Horellou P, Pradier L, Brunet I, Colin P, Mallet J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated protection of striatal neurons in an excitotoxic rat model of Huntington's disease, as demonstrated by adenoviral gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther. 1999;10(18):2987–2997. - PubMed
-
- Ciammola A, Sassone J, Cannella M, Calza S, Poletti B, Frati L, Squitieri F, Silani V. Low brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in serum of Huntington's disease patients. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2007;144(4):574–577. - PubMed
-
- Canals JM, Pineda JR, Torres-Peraza JF, Bosch M, Martin-Ibanez R, Munoz MT, Mengod G, Ernfors P, Alberch J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates the onset and severity of motor dysfunction associated with enkephalinergic neuronal degeneration in Huntington's disease. J Neurosci. 2004;24(35):7727–7739. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cepeda C, Starling AJ, Wu N, Nguyen OK, Uzgil B, Soda T, Andre VM, Ariano MA, Levine MS. Increased GABAergic function in mouse models of Huntington's disease: reversal by BDNF. J Neurosci Res. 2004;78(6):855–867. - PubMed
-
- Ciammola A, Sassone J, Cannella M, Calza S, Poletti B, Frati L, Squitieri F, Silani V. Low brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in serum of Huntington's disease patients. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2007 Jun 5;144(4):574–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

