Differential hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activation of the neuroactive steroids pregnenolone sulfate and deoxycorticosterone in healthy controls and alcohol-dependent subjects
- PMID: 18096321
- PMCID: PMC2262103
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2007.11.003
Differential hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activation of the neuroactive steroids pregnenolone sulfate and deoxycorticosterone in healthy controls and alcohol-dependent subjects
Abstract
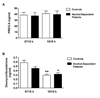
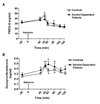
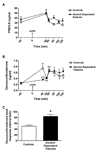
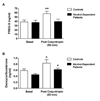
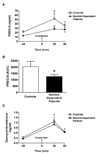
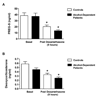
Ethanol and the neuroactive steroids have interactive neuropharmacological effects and chronic ethanol administration blunts the ethanol-induced increase in neuroactive steroid levels in rodent plasma and brain. Few studies have explored neuroactive steroid regulation in alcohol-dependent human subjects. In fact, the regulation of adrenal neuroactive steroids has not been well defined in healthy controls. We thus explored the regulation of two neuroactive steroids, pregnenolone sulfate (PREG-S) and deoxycorticosterone, by pharmacological challenges to the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in healthy controls and 1-month abstinent alcohol-dependent patients with co-occurring nicotine dependence. Plasma levels of PREG-S and deoxycorticosterone were measured by radioimmunoassay in controls and alcohol-dependent patients after challenges of naloxone, ovine corticotrophin releasing hormone (oCRH), dexamethasone, cosyntropin, and cosyntropin following high-dose dexamethasone. In addition, basal diurnal measures of both hormones were obtained. PREG-S plasma levels in healthy controls were increased by cosyntropin challenge (with and without dexamethasone pretreatment) and decreased by dexamethasone challenge. However, PREG-S concentrations were not altered by naloxone or oCRH challenges, suggesting that PREG-S is not solely regulated by hypothalamic or pituitary stimulation. Deoxycorticosterone, in contrast, is regulated by HPA challenge stimulation in a manner similar to cortisol. Alcohol-dependent patients had a blunted PREG-S response to cosyntropin (with and without dexamethasone pretreatment). Furthermore, the time to peak deoxycorticosterone response following oCRH was delayed in alcohol-dependent patients compared to controls. These results indicate that plasma PREG-S and deoxycorticosterone levels are differentially regulated by HPA axis modulation in human plasma. Further, alcohol-dependent patients show a blunted PREG-S response to adrenal stimulation and a delayed deoxycorticosterone response to oCRH challenge.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma pregnenolone levels in cynomolgus monkeys following pharmacological challenges of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2006 Aug;84(4):618-27. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2006.05.004. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2006. PMID: 16790266
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and ethanol modulation of deoxycorticosterone levels in cynomolgus monkeys.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006 Jun;186(3):293-301. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0132-2. Epub 2005 Aug 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16133132
-
Dissection of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis pathology in 1-month-abstinent alcohol-dependent men, part 2: response to ovine corticotropin-releasing factor and naloxone.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Apr;29(4):528-37. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000158939.25531.ee. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 15834217 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis modulation of GABAergic neuroactive steroids influences ethanol sensitivity and drinking behavior.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2006;8(4):463-77. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2006.8.4/amorrow. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17290803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined dexamethasone suppression-corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulation test in studies of depression, alcoholism, and suicidal behavior.ScientificWorldJournal. 2006 Oct 31;6:1398-404. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2006.251. ScientificWorldJournal. 2006. PMID: 17086345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Divergent neuroactive steroid responses to stress and ethanol in rat and mouse strains: relevance for human studies.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Sep;231(17):3257-72. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3564-8. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24770626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of ligand specificity in vertebrate corticosteroid receptors.BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Jan 14;11:14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-14. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21232159 Free PMC article.
-
Neurosteroidogenesis Today: Novel Targets for Neuroactive Steroid Synthesis and Action and Their Relevance for Translational Research.J Neuroendocrinol. 2016 Feb;28(2):12351. doi: 10.1111/jne.12351. J Neuroendocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26681259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addiction History Associates with the Propensity to Form Habits.J Cogn Neurosci. 2016 Jul;28(7):1024-38. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00953. Epub 2016 Mar 11. J Cogn Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26967944 Free PMC article.
-
Proof-of-concept trial with the neurosteroid pregnenolone targeting cognitive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Jul;34(8):1885-903. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.26. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19339966 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Adinoff B, Martin PR, Bone GH, Eckardt MJ, Roehrich L, George DT, Moss HB, Eskay R, Linnoila M, Gold PW. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning and cerebrospinal fluid corticotropin releasing hormone and corticotropin levels in alcoholics after recent and long-term abstinence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990;47:325–330. - PubMed
-
- Anthenelli RM, Maxwell RA, Geracioti TDJ, Hauger R. Stress hormone dysregulation at rest and after serotonergic stimulation among alcohol-dependent men with extended abstinence and controls. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001;25:692–703. - PubMed
-
- Barbaccia ML, Affricano D, Trabucchi M, Purdy RH, Colombo G, Agabio R, Gessa GL. Ethanol markedly increases "GABAergic" neurosteroids in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;384:R1–R2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

