Somatic inactivation of the PHD2 prolyl hydroxylase causes polycythemia and congestive heart failure
- PMID: 18096761
- PMCID: PMC2265460
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-117812
Somatic inactivation of the PHD2 prolyl hydroxylase causes polycythemia and congestive heart failure
Abstract
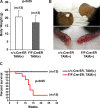
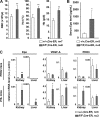
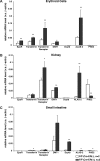
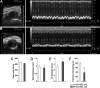
Pharmacologic activation of the heterodimeric HIF transcription factor appears promising as a strategy to treat diseases, such as anemia, myocardial infarction, and stroke, in which tissue hypoxia is a prominent feature. HIF accumulation is normally linked to oxygen availability because an oxygen-dependent posttranslational modification (prolyl hydroxylation) marks the HIFalpha subunit for polyubiquitination and destruction. Three enzymes (PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3) capable of catalyzing this reaction have been identified, although PHD2 (also called Egln1) appears to be the primary HIF prolyl hydroxylase in cell culture experiments. We found that conditional inactivation of PHD2 in mice is sufficient to activate a subset of HIF target genes, including erythropoietin, leading to striking increases in red blood cell production. Mice lacking PHD2 exhibit premature mortality associated with marked venous congestion and dilated cardiomyopathy. The latter is likely the result of hyperviscosity syndrome and volume overload, although a direct effect of chronic, high-level HIF stimulation on cardiac myocytes cannot be excluded.
Figures


References
-
- Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ. Oxygen sensing by HIF hydroxylases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:343–354. - PubMed
-
- Kaelin WG., Jr The von Hippel-Lindau protein, HIF hydroxylation, and oxygen sensing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;338:627–638. - PubMed
-
- Koivunen P, Hirsila M, Gunzler V, Kivirikko KI, Myllyharju J. Catalytic properties of the asparaginyl hydroxylase (FIH) in the oxygen sensing pathway are distinct from those of its prolyl 4-hydroxylases. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:9899–9904. - PubMed
-
- Bracken CP, Fedele AO, Linke S, et al. Cell-specific regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha stabilization and transactivation in a graded oxygen environment. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:22575–22585. - PubMed
-
- Dayan F, Roux D, Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J, Mazure NM. The oxygen sensor factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 controls expression of distinct genes through the bifunctional transcriptional character of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3688–3698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

