Characteristics of effective electronic mail messages distributed to healthcare professionals in a hospital setting
- PMID: 18096910
- PMCID: PMC2274791
- DOI: 10.1197/jamia.M2503
Characteristics of effective electronic mail messages distributed to healthcare professionals in a hospital setting
Abstract
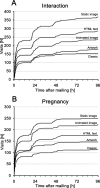
Electronic mailing systems (e-mail) are an important means to disseminate information within electronic networks. However, in large business communities including the hectic environment of hospitals it may be difficult to induce account holders to read the e-mail. In two mailings disseminated in a large university hospital we evaluated the impact of e-mail layout (three e-mail text versions, two e-mails with graphics) on the willingness of its approximately 6500 recipients to seek additional electronic information and open an integrated link. Overall access rates after 90 days were 21.1 and 23.5% with more than 70% of the respondents opening the link within 3 days. Differences between different layouts were large and artwork text, HTML text, animated GIF, and static image prompted 1.2, 1.7, 1.8, and 2.3 times more often access than the courier plain text message (p <or= 0.001). This study revealed that layout is a major determinant of the success of an information campaign.
Figures

References
-
- Neville RG, Marsden W, McCowan C, Pagliari C, Mullen H, Fannin A. A survey of GP attitudes to and experiences of email consultations Inform Prim Care 2004;12:201-205. - PubMed
-
- Olson GM, Olson JS. Human-computer interaction: Psychological aspects of the human use of computing Annu Rev Psychol 2003;54:491-516. - PubMed
-
- Wilson RF. Survey of e-mail format preferences and programs. Web Marketing Today 2003; Issue 124. http://www.wilsonweb.com/wmt8/email_format_preferences.htm 1998. Accessed May 3, 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

