Supporting patient care in the emergency department with a computerized whiteboard system
- PMID: 18096913
- PMCID: PMC2274795
- DOI: 10.1197/jamia.M2489
Supporting patient care in the emergency department with a computerized whiteboard system
Abstract
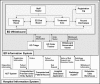
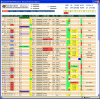
Efficient information management and communication within the emergency department (ED) is essential to providing timely and high-quality patient care. The ED whiteboard (census board) usually serves as an ED's central access point for operational and patient-related information. This article describes the design, functionality, and experiences with a computerized ED whiteboard, which has the ability to display relevant operational and patient-related information in real time. Embedded functionality, additional whiteboard views, and the integration with ED and institutional information system components, such as the computerized patient record or the provider order entry system, provide rapid access to more detailed information. As an information center, the computerized whiteboard supports our ED environment not only for providing patient care, but also for operational, educational, and research activities.
Figures

References
-
- Cordell WH, Overhage JM, Waeckerle JF. Strategies for improving information management in emergency medicine to meet clinical, research, and administrative needs. The Information Management Work Group. Ann Emerg Med 1998;31(2):172-178Feb. - PubMed
-
- Feied CF, Handler JA, Smith MS, Gillam M, Kanhouwa M, Rothenhaus T, et al. Clinical information systems: instant ubiquitous clinical data for error reduction and improved clinical outcomes Acad Emerg Med 2004;11(11):1162-1169Nov. - PubMed
-
- Derlet RW. Overcrowding in emergency departments: increased demand and decreased capacity Ann Emerg Med 2002;39(4):430-432Apr. - PubMed
-
- Derlet RW, Richards JR. Overcrowding in the nation’s emergency departments: complex causes and disturbing effects Ann Emerg Med 2000;35(1):63-68Jan. - PubMed
-
- Pham JC, Patel R, Millin MG, Kirsch TD, Chanmugam A. The effects of ambulance diversion: a comprehensive review Acad Emerg Med 2006;13(11):1220-1227Nov. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

