Rituximab therapy for juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 18097688
- PMCID: PMC2214826
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-007-0694-9
Rituximab therapy for juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
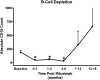
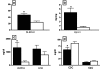
Rituximab (RTX), an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has been proposed for use in the therapy of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We present the initial long-term experience of the safety and efficacy of rituximab for treatment of SLE in children. Eighteen patients (mean age 14 +/- 3 years) with severe SLE were treated with rituximab after demonstrating resistance or toxicity to conventional regimens. There was a predominance of female (16/18) and ethnic African (13/18) patients. All had lupus nephritis [World Health Organization (WHO) classes 3-5] and systemic manifestations of vasculitis. Clinical disease activity of the SLE was scored with the SLE-disease activity index 2K (SLEDAI-2K). Patients were followed-up for an average of 3.0 +/- 1.3 years (range 0.5 to 4.8 years). B-cell depletion occurred within 2 weeks in all patients and persisted for up to 1 year in some. Clinical activity scores, double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibodies, renal function and proteinuria [urine protein to creatinine ratio (Upr/cr)] improved in 93% of the patients. Five patients required multiple courses of RTX for relapse, with B-cell repopulation. One died of infectious endocarditis related to severe immunosuppression. In conclusion, our data support the efficacy of rituximab as adjunctive treatment for SLE in children. Although rituximab was well tolerated by the majority of patients, randomized controlled trials are required to establish its long-term safety and efficacy.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

