Gold nanoparticle size controlled by polymeric Au(I) thiolate precursor size
- PMID: 18154334
- PMCID: PMC2544625
- DOI: 10.1021/ja076333e
Gold nanoparticle size controlled by polymeric Au(I) thiolate precursor size
Abstract
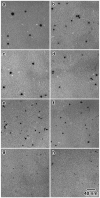
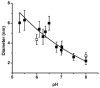
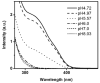
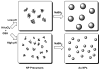
We developed a method in preparing size-controllable gold nanoparticles (Au NPs, 2-6 nm) capped with glutathione by varying the pH (between 5.5 and 8.0) of the solution before reduction. This method is based on the formation of polymeric nanoparticle precursors, Au(I)-glutathione polymers, which change size and density depending on the pH. Dynamic light scattering, size exclusion chromatography, and UV-vis spectroscopy results suggest that lower pH values favor larger and denser polymeric precursors and higher pH values favor smaller and less dense precursors. Consequently, the larger precursors led to the formation of larger Au NPs, whereas smaller precursors led to the formation of smaller Au NPs. Using this strategy, Au NPs functionalized with nickel(II) nitriloacetate (Ni-NTA) group were prepared by a mixed-ligand approach. These Ni-NTA functionalized Au NPs exhibited specific binding to 6x-histidine-tagged Adenovirus serotype 12 knob proteins, demonstrating their utility in biomolecular labeling applications.
Figures

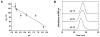

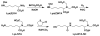



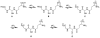

References
-
- Salem AK, Searson PC, Leong KW. Nature Mater. 2003;2:668–671. - PubMed
-
- Shukla S, Priscilla A, Banerjee M, Bhonde RR, Ghatak J, Satyam PV, Sastry M. Chem Mater. 2005;17:5000–5005.
-
- Krämer S, Xie H, Gaff J, Williamson JR, Tkachenko AG, Nouri N, Feldheim DA, Feldheim DL. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:5388–5395. - PubMed
-
- Handley DA. In: Colloidal Gold: Principles, Methods, and Applications. Hayat MA, editor. Vol. 1. Academic Press, Inc.; San Diego: 1989. pp. 13–30.
-
- Frenkel AI, Nemzer S, Pister I, Soussan L, Harris T. J Chem Phys. 2005;123:184701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

