Binding to DPF-motif by the POB1 EH domain is responsible for POB1-Eps15 interaction
- PMID: 18154663
- PMCID: PMC2238750
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-8-29
Binding to DPF-motif by the POB1 EH domain is responsible for POB1-Eps15 interaction
Abstract
Background: Eps15 homology (EH) domains are protein interaction modules binding to peptides containing Asn-Pro-Phe (NPF) motifs and mediating critical events during endocytosis and signal transduction. The EH domain of POB1 associates with Eps15, a protein characterized by a striking string of DPF triplets, 15 in human and 13 in mouse Eps15, at the C-terminus and lacking the typical EH-binding NPF motif.
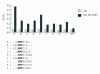
Results: By screening a multivalent nonapeptide phage display library we have demonstrated that the EH domain of POB1 has a different recognition specificity since it binds to both NPF and DPF motifs. The region of mouse Eps15 responsible for the interaction with the EH domain of POB1 maps within a 18 amino acid peptide (residues 623-640) that includes three DPF repeats. Finally, mutational analysis in the EH domain of POB1, revealed that several solvent exposed residues, while distal to the binding pocket, mediate specific recognition of binding partners through both hydrophobic and electrostatic contacts.
Conclusion: In the present study we have analysed the binding specificity of the POB1 EH domain. We show that it differs from other EH domains since it interacts with both NPF- and DPF-containing sequences. These unusual binding properties could be attributed to a different conformation of the binding pocket that allows to accommodate negative charges; moreover, we identified a cluster of solvent exposed Lys residues, which are only found in the EH domain of POB1, and influence binding to both NPF and DPF motifs. The characterization of structures of the DPF ligands described in this study and the POB1 EH domain will clearly determine the involvement of the positive patch and the rationalization of our findings.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanism of NPF recognition by EH domains.Nat Struct Biol. 2000 Nov;7(11):1018-22. doi: 10.1038/80924. Nat Struct Biol. 2000. PMID: 11062555
-
Epsin binds to the EH domain of POB1 and regulates receptor-mediated endocytosis.Oncogene. 1999 Oct 21;18(43):5915-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202974. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10557078
-
Solution structure of Eps15's third EH domain reveals coincident Phe-Trp and Asn-Pro-Phe binding sites.Biochemistry. 2000 Apr 18;39(15):4309-19. doi: 10.1021/bi9927383. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10757979
-
EH and UIM: endocytosis and more.Sci STKE. 2003 Dec 16;2003(213):re17. doi: 10.1126/stke.2132003re17. Sci STKE. 2003. PMID: 14679291 Review.
-
Recycling and EH domain proteins at the synapse.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005 Sep;49(2):416-28. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2005.06.002. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005. PMID: 16054223 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular dynamics simulation of the interactions between EHD1 EH domain and multiple peptides.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015 Oct;16(10):883-96. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1500106. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015. PMID: 26465136 Free PMC article.
-
The central proline rich region of POB1/REPS2 plays a regulatory role in epidermal growth factor receptor endocytosis by binding to 14-3-3 and SH3 domain-containing proteins.BMC Biochem. 2008 Jul 22;9:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-9-21. BMC Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18647389 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into the interaction of proteins containing NPF, DPF, and GPF motifs with the C-terminal EH-domain of EHD1.Protein Sci. 2009 Dec;18(12):2471-9. doi: 10.1002/pro.258. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19798736 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization and Corroboration of the Regulatory Pathway of p42.3 Protein in the Pathogenesis of Gastric Carcinoma.Comput Math Methods Med. 2015;2015:683679. doi: 10.1155/2015/683679. Epub 2015 May 28. Comput Math Methods Med. 2015. PMID: 26106439 Free PMC article.
-
Promiscuous and multivalent interactions between Eps15 and partner protein Dab2 generate a complex interaction network.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 21;16(1):7783. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-63090-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40841375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carbone R, Fré S, Iannolo G, Belleudi F, Mancini P, Pelicci PG, Torrisi MR, Di Fiore PP. eps15 and eps15R are essential components of the endocytic pathway. Cancer Res. 1997;57:5498–5504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

