Production of highly knotted DNA by means of cosmid circularization inside phage capsids
- PMID: 18154674
- PMCID: PMC2231350
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-7-94
Production of highly knotted DNA by means of cosmid circularization inside phage capsids
Abstract
Background: The formation of DNA knots is common during biological transactions. Yet, functional implications of knotted DNA are not fully understood. Moreover, potential applications of DNA molecules condensed by means of knotting remain to be explored. A convenient method to produce abundant highly knotted DNA would be highly valuable for these studies.
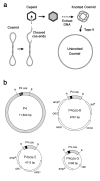
Results: We had previously shown that circularization of the 11.2 kb linear DNA of phage P4 inside its viral capsid generates complex knots by the effect of confinement. We demonstrate here that this mechanism is not restricted to the viral genome. We constructed DNA cosmids as small as 5 kb and introduced them inside P4 capsids. Such cosmids were then recovered as a complex mixture of highly knotted DNA circles. Over 250 mug of knotted cosmid were typically obtained from 1 liter of bacterial culture.
Conclusion: With this biological system, DNA molecules of varying length and sequence can be shaped into very complex and heterogeneous knotted forms. These molecules can be produced in preparative amounts suitable for systematic studies and applications.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel topologically knotted DNA from bacteriophage P4 capsids: studies with DNA topoisomerases.Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3979-89. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3979. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981. PMID: 6272191 Free PMC article.
-
Knotting probability of DNA molecules confined in restricted volumes: DNA knotting in phage capsids.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 16;99(8):5373-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.032095099. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11959991 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of knotted DNA from coliphage P4.Methods Mol Biol. 1999;94:69-74. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-259-7:69. Methods Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 12844863 No abstract available.
-
[Distributions of circular DNA according its topological states].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2001 Mar-Apr;35(2):285-97. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2001. PMID: 11357411 Review. Russian.
-
Structure and assembly of bacteriophage lambda.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;78:69-110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66800-5_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977. PMID: 340151 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Topological patterns in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of DNA knots.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Oct 6;112(40):E5471-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506907112. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26351668 Free PMC article.
-
The Rabl configuration limits topological entanglement of chromosomes in budding yeast.Sci Rep. 2019 May 1;9(1):6795. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42967-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31043625 Free PMC article.
-
Ring Polymers: Threadings, Knot Electrophoresis and Topological Glasses.Polymers (Basel). 2017 Aug 8;9(8):349. doi: 10.3390/polym9080349. Polymers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30971026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effective stiffening of DNA due to nematic ordering causes DNA molecules packed in phage capsids to preferentially form torus knots.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jun;40(11):5129-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks157. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22362732 Free PMC article.
-
Synergy of topoisomerase and structural-maintenance-of-chromosomes proteins creates a universal pathway to simplify genome topology.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 23;116(17):8149-8154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815394116. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30962387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shishido K, Ishii S, Komiyama N. The presence of the region on pBR322 that encodes resistance to tetracycline is responsible for high levels of plasmid DNA knotting in Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I deletion mutant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17:9749–7959. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9749. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

