A novel method of 2-channel dual-pulse gastric electrical stimulation improves solid gastric emptying in dogs
- PMID: 18154935
- PMCID: PMC2677293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.07.001
A novel method of 2-channel dual-pulse gastric electrical stimulation improves solid gastric emptying in dogs
Abstract
Background: Gastric electrical stimulation (GES) is known to improve vomiting with short pulses, normalize dysrhythmia with long pulses, and accelerate gastric emptying with 2 channels. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of a new method GES, namely, 2-channel GES with dual pulses on gastric emptying of solids as well as gastric dysrhythmia and emetic responses.
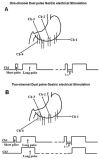
Methods: Seven beagle dogs implanted with 4 pairs of electrodes were studied. A novel method of GES was proposed: 2-channel dual-pulse GES in which each stimulus was composed of a short pulse followed with a long pulse, and stimulation was delivered at 2 different locations. The study was performed to test the effects of this new method of GES on vasopressin-induced delayed gastric emptying of solids, gastric dysrhythmia, and emetic responses.
Results: (1) Vasopressin-induced gastric dysrhythmia and emetic responses, as well as delayed gastric emptying of solids (P < .01). (2) Two-channel, but not 1-channel, dual-pulse GES was able to accelerate vasopressin-induced delayed gastric emptying of solids. (3) Both 1- and 2-channel dual-pulse GES was capable of improving dysrhythmia and emetic responses (P < .01).
Conclusions: The novel method of 2-channel dual-pulse GES is capable of accelerating gastric emptying of solids and improving dysrhythmia and emetic responses induced by vasopressin. This new method of GES may have a potential for gastroparesis.
References
-
- The American Gastroenterological Association Clinical Practice Committee. American Gastroenterological Association Technical Review on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1592–1622. - PubMed
-
- Hornbuckle K, Barnett JL. The diagnosis and work-up of the patient with gastroparesis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;30:117–24. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz M, O’Donovan D, Jones KL, Feinle C, Rayner CK, Samsom M. Gastric emptying in diabetes: clinical significance and treatment. Diabetic Medicine. 2002;19(3):177–94. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz M, Edelbroek M, Fraser R, Maddox A, Wishart J. Disordered gastric motor function in diabetes mellitus. Recent insights into prevalence, pathophysiology, clinical relevance, and treatment Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991;26:673–684. - PubMed
-
- Zitomer BR, Gramm HF, Kozak GP. Gastric neuropathy in diabetes mellitus: Clinical and radiographic observations. Metabolism. 1968;17:199–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources