The rostral anterior cingulate cortex modulates the efficiency of amygdala-dependent fear learning
- PMID: 18155183
- PMCID: PMC2880388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.10.022
The rostral anterior cingulate cortex modulates the efficiency of amygdala-dependent fear learning
Abstract
Background: The rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC) and the amygdala consistently emerge from neuroimaging studies as brain regions crucially involved in normal and abnormal fear processing. To date, however, the role of the rACC specifically during the acquisition of auditory fear conditioning still remains unknown. The aim of this study is to investigate a possible top-down control of a specific rACC sub-region over amygdala activation during pavlovian fear acquisition.
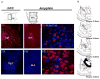
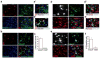
Methods: We performed excitotoxic lesions, temporal inactivation, and activation of a specific sub-region of the rACC that we identified by tracing studies as supporting most of the connectivity with the basolateral amygdala (r(Amy)-ACC). The effects of these manipulations over amygdala function were investigated with a classical tone-shock associative fear conditioning paradigm in the rat.
Results: Excitotoxic lesions and transient inactivation of the r(Amy)-ACC pre-training selectively produced deficits in the acquisition of the tone-shock associative learning (but not context). This effect was specific for the acquisition phase. However, the deficit was found to be transient and could be overcome by overtraining. Conversely, pre-training transient activation of the r(Amy)-ACC facilitated associative learning and increased fear expression.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that a subregion of the rACC is key to gating the efficiency of amygdala-dependent auditory fear conditioning learning. Because r(Amy)-ACC inputs were confirmed to be glutamatergic, we propose that recruitment of this brain area might modulate overall basolateral amygdala excitatory tone during conditioned stimulus-unconditioned stimulus concomitant processing. In the light of clinical research, our results provide new insight on the effect of inappropriate rACC recruitment during emotional events.
Figures
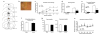

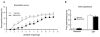
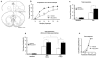
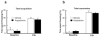
Similar articles
-
Anterior cingulate cortex and its input to the basolateral amygdala control innate fear response.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 16;9(1):2744. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05090-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30013065 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Arc/Arg 3.1 protein expression in the basolateral amygdala following auditory trace-cued fear conditioning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013 Nov;106:127-33. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013. PMID: 23891993
-
Differential contribution of amygdala and hippocampus to cued and contextual fear conditioning.Behav Neurosci. 1992 Apr;106(2):274-85. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.106.2.274. Behav Neurosci. 1992. PMID: 1590953
-
Interplay of amygdala and cingulate plasticity in emotional fear.Neural Plast. 2011;2011:813749. doi: 10.1155/2011/813749. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Neural Plast. 2011. PMID: 21912749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural circuits and mechanisms involved in Pavlovian fear conditioning: a critical review.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006;30(2):188-202. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.06.005. Epub 2005 Aug 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006. PMID: 16120461 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural signals implicated in the processing of appetitive and aversive events in social and non-social contexts.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 Aug 3;16:926388. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2022.926388. eCollection 2022. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35993086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic ketamine impairs fear conditioning and produces long-lasting reductions in auditory evoked potentials.Neurobiol Dis. 2009 Aug;35(2):311-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.05.012. Epub 2009 May 23. Neurobiol Dis. 2009. PMID: 19467327 Free PMC article.
-
Executive dysfunction and cortical variations among intimate partner violence perpetrators and the association with sexism.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2024 Jul 4;19(1):nsae046. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsae046. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38915189 Free PMC article.
-
The role of working memory and declarative memory in trace conditioning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016 Oct;134 Pt B(Pt B):193-209. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27422017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anterior cingulate cortex and its input to the basolateral amygdala control innate fear response.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 16;9(1):2744. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05090-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30013065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fendt M, Fanselow MS. The neuroanatomical and neurochemical basis of conditioned fear. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1999;23:743–760. - PubMed
-
- Aguado L. Neuroscience of Pavlovian conditioning: a brief review. Span J Psychol. 2003;6:155–167. - PubMed
-
- LeDoux JE. Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2000;23:155–184. - PubMed
-
- Rauch SL, Shin LM, Wright CI. Neuroimaging studies of amygdala function in anxiety disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;985:389–410. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

