The structure of the C-terminal actin-binding domain of talin
- PMID: 18157087
- PMCID: PMC2168396
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601965
The structure of the C-terminal actin-binding domain of talin
Abstract
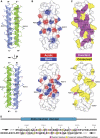
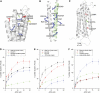
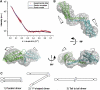
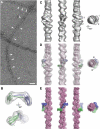
Talin is a large dimeric protein that couples integrins to cytoskeletal actin. Here, we report the structure of the C-terminal actin-binding domain of talin, the core of which is a five-helix bundle linked to a C-terminal helix responsible for dimerisation. The NMR structure of the bundle reveals a conserved surface-exposed hydrophobic patch surrounded by positively charged groups. We have mapped the actin-binding site to this surface and shown that helix 1 on the opposite side of the bundle negatively regulates actin binding. The crystal structure of the dimerisation helix reveals an antiparallel coiled-coil with conserved residues clustered on the solvent-exposed face. Mutagenesis shows that dimerisation is essential for filamentous actin (F-actin) binding and indicates that the dimerisation helix itself contributes to binding. We have used these structures together with small angle X-ray scattering to derive a model of the entire domain. Electron microscopy provides direct evidence for binding of the dimer to F-actin and indicates that it binds to three monomers along the long-pitch helix of the actin filament.
Figures

References
-
- Brett TJ, Legendre-Guillemin V, McPherson PS, Fremont DH (2006) Structural definition of the F-actin-binding THATCH domain from HIP1R. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13: 121–130 - PubMed
-
- Critchley DR (2004) Cytoskeletal proteins talin and vinculin in integrin-mediated adhesion. Biochem Soc Trans 32: 831–836 - PubMed
-
- Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6: 277–293 - PubMed
-
- Dominguez R (2004) Actin-binding proteins—a unifying hypothesis. Trends Biochem Sci 29: 572–578 - PubMed
-
- Egelman EH (2000) A robust algorithm for the reconstruction of helical filaments using single-particle methods. Ultramicroscopy 85: 225–234 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

