A beta-catenin gradient links the clock and wavefront systems in mouse embryo segmentation
- PMID: 18157121
- PMCID: PMC7391962
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1679
A beta-catenin gradient links the clock and wavefront systems in mouse embryo segmentation
Abstract
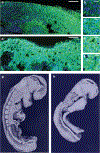
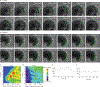
Rhythmic production of vertebral precursors, the somites, causes bilateral columns of embryonic segments to form. This process involves a molecular oscillator--the segmentation clock--whose signal is translated into a spatial, periodic pattern by a complex signalling gradient system within the presomitic mesoderm (PSM). In mouse embryos, Wnt signalling has been implicated in both the clock and gradient mechanisms, but how the Wnt pathway can perform these two functions simultaneously remains unclear. Here, we use a yellow fluorescent protein (YFP)-based, real-time imaging system in mouse embryos to demonstrate that clock oscillations are independent of beta-catenin protein levels. In contrast, we show that the Wnt-signalling gradient is established through a nuclear beta-catenin protein gradient in the posterior PSM. This gradient of nuclear beta-catenin defines the size of the oscillatory field and controls key aspects of PSM maturation and segment formation, emphasizing the central role of Wnt signalling in this process.
Figures



References
-
- Palmeirim I, Henrique D, Ish-Horowicz D & Pourquié O Avian hairy gene expression identifies a molecular clock linked to vertebrate segmentation and somitogenesiss. Cell 91, 639–648 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Aulehla A et al. Wnt3a plays a major role in the segmentation clock controlling somitogenesis. Dev. Cell 4, 395–406 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Dequeant ML et al. A complex oscillating network of signalling genes underlies the mouse segmentation clock. Science 314, 1595–1598 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Satoh W, Gotoh T, Tsunematsu Y, Aizawa S & Shimono A Sfrp1 and Sfrp2 regulate anteroposterior axis elongation and somite segmentation during mouse embryogenesis. Development 133, 989–999 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

