Current hepatitis A status in Canada
- PMID: 18159360
- PMCID: PMC2094846
- DOI: 10.1155/2001/834670
Current hepatitis A status in Canada
Abstract
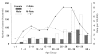
Hepatitis A, caused by the hepatitis A virus, occurs most frequently in developing countries, but also causes sporadic cases or outbreaks in industrialized countries. The most common route of transmission is fecal-oral. The incidence of hepatitis A varies with geography, and economic and environmental conditions. The epidemiological pattern of the disease has changed with improvements in hygiene and economic conditions. The incidence and prevalence of hepatitis A has decreased, while the average age of exposure and subsequent infection has increased. The present report describes the current status of hepatitis A in Canada. The incidence rate of reported cases in Canada varies from over 10/100,000 (1991) to 3.6/100,000 (1998), and is higher in males, 4.7/100,000 (1998), than in females, 2.5/100,000 (1998). The highest reported hepatitis A rates are in age groups 30 to 39 years and 40 to 59 years, and in British Columbia. Such information is important for assessing current immunization approaches and for decision-making about new preventive strategies against hepatitis A in Canada.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Hepatitis A; Hepatitis A virus; Viral hepatitis.
Figures


References
-
- Margolis HS, Alter MJ, Hadler SC. Viral hepatitis. In: Evans AS, Kaslow R, eds. Viral Infections of Humans: Epidemiology and Control, 4th edn. New Haven:Plenum Publishing, 1997:363-418.
-
- Provost PJ, Wolanski BS, Miller WJ, Ittensohn OL, McAleer WJ, Hilleman MR. Physical, chemical and morphologic dimensions of human hepatitis A virus strain CR326 (38578).Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1975;148:532-9. - PubMed
-
- Hadler SC. Global impact of hepatitis A virus infection. In: Hollinger FB, Lemon SM, Margolis H, eds. Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease: Proceedings of the 1990 International Symposium on Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease.Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1991:14-20.
-
- Bower WA, Nainan OV, Han X, Margolis HS. Duration of viremia in hepatitis A virus infection.J Infect Dis 2000;182:12-7. - PubMed
-
- Koff RS. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of hepatitis A virus infection.Vaccine 1992;10(Suppl 1):S15-7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
