Simultaneous measurements of fast optical and proton current kinetics in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle using an enhanced spectrophotometer
- PMID: 18160131
- PMCID: PMC2836842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jprot.2007.11.004
Simultaneous measurements of fast optical and proton current kinetics in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle using an enhanced spectrophotometer
Abstract
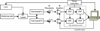
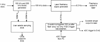
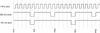
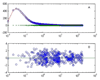
A one-of-a-kind high speed optical multichannel spectrometer was designed and built at NIH and described in this journal in 1997 [J.W. Cole, R.W. Hendler, P.D. Smith, H.A. Fredrickson, T.J. Pohida, W.S. Friauf. A high speed optical multichannel analyzer. J Biochem Biophys Methods 1997;35:16-174.]. The most unique aspect of this instrument was the ability to follow an entire time course from a single activation using a single sample. The instrument has been used to study rapid kinetic processes in the photon-driven bacteriorhodopsin photocycle and electron transport from cytochrome c to cytochrome aa3 and from cytochrome aa3 to oxygen. The present paper describes a second generation instrument with a number of important enhancements which significantly improve its capabilities for multichannel kinetic studies. An example application is presented in which the kinetics of photon-induced proton flow across the biological membrane is measured simultaneously with the individual steps of the photocycle determined optically. Matching the time constants for the two processes indicates which molecular transformations are associated with major proton movements.
Figures



References
-
- Shrager RI, Hendler RW. Titration of individual components in a mixture with resolution of difference spectra, pK’s, and redox titrations. Anal. Chem. 1982;54:1147–1152.
-
- Cole JW, Hendler RW, Smith PD, Fredrickson HA, Pohida TJ, Friauf WS. A high speed optical multichannel analyzer. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods. 1997;35:161–174. - PubMed
-
- Hendler RW, Dancshazy Zs, Bose S, Shrager RI, Tokaji Zs. Influence of excitation energy on the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1994;33:4604–4610. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadyay AK, Bose S, Hendler RW. Membrane-mediated control of the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1994;33:10889–10895. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadyay AK, Dracheva S, Bose S, Hendler RW. Control of the integral membrane proton pump, bacteriorhodopsin, by purple membrane lipids of Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry. 1996;35:9245–9252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

