RNA structure modulates splicing efficiency at the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 major splice donor
- PMID: 18160437
- PMCID: PMC2258995
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01479-07
RNA structure modulates splicing efficiency at the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 major splice donor
Abstract
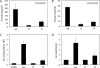
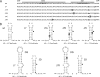
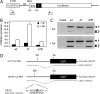
The untranslated leader of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA genome encodes essential sequence and structural motifs that control various replication steps. The 5' splice site or splice donor (SD) is embedded in a semistable hairpin, but the function of this structure is unknown. We stabilized this SD hairpin by creating an additional base pair and demonstrated a severe HIV-1 replication defect. A splicing defect was apparent in RNA analyses of virus-infected cells and cells transfected with appropriate reporter constructs. We selected multiple virus revertants in search for interesting second-site escape pathways. Most revertants acquired an additional mutation that modulated the stability of the mutant SD hairpin. One revertant acquired a single nucleotide change in the upstream DIS hairpin. We demonstrate that a novel SD site is created by this upstream mutation, which obviously reduces the number of leader nucleotides that are included in spliced HIV-1 transcripts. These results suggest a novel role of RNA structure in the regulation of HIV-1 splicing.
Figures

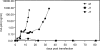


References
-
- Abbink, T. E. M., and B. Berkhout. 2003. A novel long distance base-pairing interaction in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA occludes the gag start codon. J. Biol. Chem. 27811601-11611. - PubMed
-
- Abbink, T. E. M., M. Ooms, P. C. J. Haasnoot, and B. Berkhout. 2005. The HIV-1 leader RNA conformational switch regulates RNA dimerization but does not regulate mRNA translation. Biochemistry 449058-9066. - PubMed
-
- Beerens, N., F. Groot, and B. Berkhout. 2001. Initiation of HIV-1 reverse transcription is regulated by a primer activation signal. J. Biol. Chem. 27631247-31256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

