The thyroid hormone mimetic compound KB2115 lowers plasma LDL cholesterol and stimulates bile acid synthesis without cardiac effects in humans
- PMID: 18160532
- PMCID: PMC2206593
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705286104
The thyroid hormone mimetic compound KB2115 lowers plasma LDL cholesterol and stimulates bile acid synthesis without cardiac effects in humans
Abstract
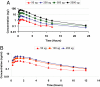
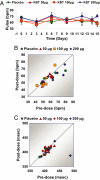
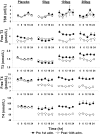
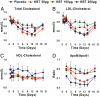
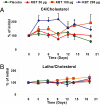
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is a major problem despite the availability of drugs that influence major risk factors. New treatments are needed, and there is growing interest in therapies that may have multiple actions. Thyroid hormone modulates several cardiovascular risk factors and delays atherosclerosis progression in humans. However, use of thyroid hormone is limited by side effects, especially in the heart. To overcome this limitation, pharmacologically selective thyromimetics that mimic metabolic effects of thyroid hormone and bypass side effects are under development. In animal models, such thyromimetics have been shown to stimulate cholesterol elimination through LDL and HDL pathways and decrease body weight without eliciting side effects. We report here studies on a selective thyromimetic [KB2115; (3-[[3,5-dibromo-4-[4-hydroxy-3-(1-methylethyl)-phenoxy]-phenyl]-amino]-3-oxopropanoic acid)] in humans. In moderately overweight and hypercholesterolemic subjects KB2115 was found to be safe and well tolerated and elicited up to a 40% lowering of total and LDL cholesterol after 14 days of treatment. Bile acid synthesis was stimulated without evidence of increased cholesterol production, indicating that KB2115 induced net cholesterol excretion. KB2115 did not provoke detectable effects on the heart, suggesting that the pharmacological selectivity observed in animal models translates to humans. Thus, selective thyromimetics deserve further study as agents to treat dyslipidemia and other risk factors for atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A.B., J.K., K.M., B.C., J.M., S.R., N.G., and C.M.A. are employees of Karo Bio AB. B.A. and J.D.B. have proprietary interests in and serve as consultants to Karo Bio AB. F.S. is employed by Berzelius Clinical Research Center AB.
Figures
Comment in
-
Thyroid mimetic as an option for lowering low-density lipoprotein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jan 15;105(2):409-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705959104. Epub 2008 Jan 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18187579 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Grundy SM. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:295–309. - PubMed
-
- Cappola AR, Ladenson PW. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:2438–2444. - PubMed
-
- Gwinup G, Poucher R. Am J Med Sci. 1967;254:416–420. - PubMed
-
- Monzani F, Caraccio N, Kozakowa M, Dardano A, Vittone F, Virdis A, Taddei S, Palombo C, Ferrannini E. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2099–2106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

