Proprioceptive sensory neuropathy in mice with a mutation in the cytoplasmic Dynein heavy chain 1 gene
- PMID: 18160659
- PMCID: PMC6673431
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4338-07.2007
Proprioceptive sensory neuropathy in mice with a mutation in the cytoplasmic Dynein heavy chain 1 gene
Abstract
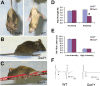
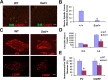
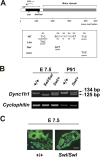
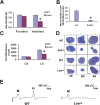
Mice heterozygous for the radiation-induced Sprawling (Swl) mutation display an early-onset sensory neuropathy with muscle spindle deficiency. The lack of an H reflex despite normal motor nerve function in the hindlimbs of these mutants strongly suggests defective proprioception. Immunohistochemical analyses reveal that proprioceptive sensory neurons are severely compromised in the lumbar dorsal root ganglia of newborn Swl/+ mice, whereas motor neuron numbers remain unaltered even in aged animals. We have used positional cloning to identify a nine base-pair deletion in the cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain 1 gene (Dync1h1) in this mutant. Furthermore, we demonstrate that Loa/+ mice, which have previously been shown to carry a missense point mutation in Dync1h1 that results in late-onset motor neuron loss, also present with a severe, early-onset proprioceptive sensory neuropathy. Interestingly, in contrast to the Loa mutation, the Swl mutation does not delay disease progression in a motor neuron disease mouse model overexpressing a human mutant superoxide dismutase (SOD1(G93A)) transgene. Together, we provide in vivo evidence that distinct mutations in cytoplasmic dynein can either result in a pure sensory neuropathy or in a sensory neuropathy with motor neuron involvement.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad-Annuar A, Shah P, Hafezparast M, Hummerich H, Witherden AS, Morrison KE, Shaw PJ, Kirby J, Warner TT, Crosby A, Proukakis C, Wilkinson P, Orrell RW, Bradley L, Martin JE, Fisher EM. No association with common Caucasian genotypes in exons 8, 13 and 14 of the human cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain gene (DNCHC1) and familial motor neuron disorders. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2003;4:150–157. - PubMed
-
- Barakat-Walter I, Riederer BM. Triiodothyronine and nerve growth factor are required to induce cytoplasmic dynein expression in rat dorsal root ganglion cultures. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1996;96:109–119. - PubMed
-
- Brook GA, Duchen LW. End-plates, transmission and contractile characteristics of muscles without spindles in the hereditary sensory neuropathy of the Sprawling mouse. Brain. 1990;113:867–891. - PubMed
-
- Buchman VL, Davies AM. Different neurotrophins are expressed and act in a developmental sequence to promote the survival of embryonic sensory neurons. Development. 1993;118:989–1001. - PubMed
-
- Celio MR. Calbindin D-28k and parvalbumin in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience. 1990;35:375–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
