ATP binding by monarch-1/NLRP12 is critical for its inhibitory function
- PMID: 18160710
- PMCID: PMC2258772
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01468-07
ATP binding by monarch-1/NLRP12 is critical for its inhibitory function
Abstract
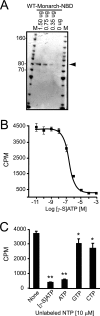
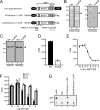
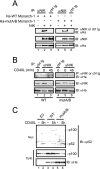
The recently discovered nucleotide binding domain-leucine rich repeat (NLR) gene family is conserved from plants to mammals, and several members are associated with human autoinflammatory or immunodeficiency disorders. This family is defined by a central nucleotide binding domain that contains the highly conserved Walker A and Walker B motifs. Although the nucleotide binding domain is a defining feature of this family, it has not been extensively studied in its purified form. In this report, we show that purified Monarch-1/NLRP12, an NLR protein that negatively regulates NF-kappaB signaling, specifically binds ATP and exhibits ATP hydrolysis activity. Intact Walker A/B motifs are required for this activity. These motifs are also required for Monarch-1 to undergo self-oligomerization, Toll-like receptor- or CD40L-activated association with NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) and interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1), degradation of NIK, and inhibition of IRAK-1 phosphorylation. The stable expression of a Walker A/B mutant in THP-1 monocytes results in increased production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines to an extent comparable to that in cells in which Monarch-1 is silenced via short hairpin RNA. The results of this study are consistent with a model wherein ATP binding regulates the anti-inflammatory activity of Monarch-1.
Figures



References
-
- Aksentijevich, I., M. Nowak, M. Mallah, J. J. Chae, W. T. Watford, S. R. Hofmann, L. Stein, R. Russo, D. Goldsmith, P. Dent, H. F. Rosenberg, F. Austin, E. F. Remmers, J. E. Balow, Jr., S. Rosenzweig, H. Komarow, N. G. Shoham, G. Wood, J. Jones, N. Mangra, H. Carrero, B. S. Adams, T. L. Moore, K. Schikler, H. Hoffman, D. J. Lovell, R. Lipnick, K. Barron, J. J. O'Shea, D. L. Kastner, and R. Goldbach-Mansky. 2002. De novo CIAS1 mutations, cytokine activation, and evidence for genetic heterogeneity in patients with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID): a new member of the expanding family of pyrin-associated autoinflammatory diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 463340-3348. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albrecht, M., and F. L. Takken. 2006. Update on the domain architectures of NLRs and R proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 339459-462. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B. 2001. Autoimmunity and apoptosis: the Crohn's connection. Immunity 155-14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
