Expression of junctional proteins in choroid plexus epithelial cell lines: a comparative study
- PMID: 18162136
- PMCID: PMC2241822
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-8454-4-11
Expression of junctional proteins in choroid plexus epithelial cell lines: a comparative study
Abstract
Background: There is an increasing interest in using choroid plexus (CP) epithelial cell lines to study the properties of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB). Currently, there are three major CP-derived cell lines available. Z310 and TR-CSFB3, two immortalized cell lines carrying the simian virus 40 large T-antigen gene, were derived from rat CP epithelium, whereas the CPC-2 cell line was derived from human CP carcinoma. Although these cell lines have previously been used in various functional studies, the expression of adherens junction (AJ) and tight junction (TJ) proteins in these epithelial cells has not been systematically studied. Accordingly, in the present study, we sought to characterize the expression of these junctional proteins in these three cell lines.
Methods: The cells were grown in six-well cell culture plates. Reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting, and immunocytochemistry were used to characterize the expression of AJ and TJ proteins in the CP cell lines.
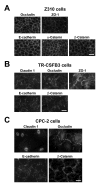
Results: Z310 and TR-CSFB3 cells expressed a TJ protein, occludin, and its cytosolic binding partner, zonula occludens 1, as well as an AJ protein, E-cadherin, and beta-catenin, a cytoplasmic protein that interacts with E-cadherin. However, the expression of occludin and E-cadherin in TR-CSFB3 cells at both the mRNA and protein level was weaker than that found in Z301 cells. The immunocytochemical analysis also demonstrated that the staining pattern for these junctional proteins in TR-CSFB3 cells was discontinuous and the staining intensity was weaker than that observed in Z310 cells. The message for claudin 1 and claudin 2 was expressed at low levels in TR-CSFB3 cells and these cells were weakly immunopositive for claudin 1. In comparison, the message for these TJ proteins could not be detected in Z310 cells. CPC-2 cells expressed occludin, which was localized to areas of cell-cell contact, but the staining pattern for this TJ protein was found to be variable and irregular. Although CPC-2 cells expressed mRNA for claudin 1, claudin 2, and claudin 11, only claudin 1 was expressed at the protein level and it was localized to the nuclei rather than to areas of cell-cell contact. An AJ protein, E-cadherin, was also found to be mislocalized in CPC-2 cells, even though its cytosolic binding partner, beta-catenin, was restricted to areas of cell-cell contact, as in normal CP.
Conclusion: The three CP cell lines analyzed in this study vary considerably with regard to the expression of AJ and TJ proteins, which is likely reflected by different barrier properties of these in vitro models of BCSFB.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neutrophil transmigration in inflammatory bowel disease is associated with differential expression of epithelial intercellular junction proteins.Am J Pathol. 2001 Dec;159(6):2001-9. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63051-9. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11733350 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Z310 cells as an in vitro blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier model: tight junction proteins and transport properties.Toxicol In Vitro. 2008 Feb;22(1):190-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2007.07.007. Epub 2007 Jul 28. Toxicol In Vitro. 2008. PMID: 17825520 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of immortalized choroid plexus epithelial cell lines for studies of transport processes across the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier.Cerebrospinal Fluid Res. 2010 Aug 12;7:11. doi: 10.1186/1743-8454-7-11. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res. 2010. PMID: 20704740 Free PMC article.
-
The epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease: potential role of endocytosis of junctional proteins in barrier disruption.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;263:115-24; discussion 124-32, 211-8. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15669638 Review.
-
A new in vitro model for blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier transport studies: an immortalized choroid plexus epithelial cell line derived from the tsA58 SV40 large T-antigen gene transgenic rat.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004 Oct 14;56(12):1875-85. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2004.07.013. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004. PMID: 15381338 Review.
Cited by
-
E-Cadherin Is Expressed in Epithelial Cells of the Choroid Plexus in Human and Mouse Brains.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Sep 26;45(10):7813-7826. doi: 10.3390/cimb45100492. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37886936 Free PMC article.
-
The status of intercellular junctions in established lens epithelial cell lines.Mol Vis. 2012;18:2937-46. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 23288986 Free PMC article.
-
SPINT1 Expressed in Epithelial Cells of Choroid Plexus in Human and Mouse Brains.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 27;26(11):5130. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115130. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507942 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling immune functions of the mouse blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier in vitro: primary rather than immortalized mouse choroid plexus epithelial cells are suited to study immune cell migration across this brain barrier.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016 Jan 29;13:2. doi: 10.1186/s12987-016-0027-0. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016. PMID: 26833402 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the human choroid plexus in vitro.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2013 Feb 7;10(1):10. doi: 10.1186/2045-8118-10-10. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2013. PMID: 23391221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kitazawa T, Hosoya K, Watanabe M, Takashima T, Ohtsuki S, Takanaga H, Ueda M, Yanai N, Obinata M, Terasaki T. Characterization of the amino acid transport of new immortalized choroid plexus epithelial cell lines: a novel in vitro system for investigating transport functions at the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Pharm Res. 2001;18:16–22. doi: 10.1023/A:1011014424212. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

