Degradation of MEPE, DMP1, and release of SIBLING ASARM-peptides (minhibins): ASARM-peptide(s) are directly responsible for defective mineralization in HYP
- PMID: 18162525
- PMCID: PMC2276704
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2007-1205
Degradation of MEPE, DMP1, and release of SIBLING ASARM-peptides (minhibins): ASARM-peptide(s) are directly responsible for defective mineralization in HYP
Abstract
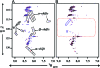
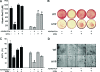
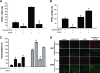
Mutations in PHEX (phosphate-regulating gene with homologies to endopeptidases on the X chromosome) and DMP1 (dentin matrix protein 1) result in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (HYP) and autosomal-recessive hypophosphatemic-rickets (ARHR), respectively. Specific binding of PHEX to matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein (MEPE) regulates the release of small protease-resistant MEPE peptides [acidic serine- and aspartate-rich MEPE-associated motif (ASARM) peptides]. ASARM peptides are potent inhibitors of mineralization (minhibins) that also occur in DMP1 [MEPE-related small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoprotein (SIBLING) protein]. It is not known whether these peptides are directly responsible for the mineralization defect. We therefore used a bone marrow stromal cell (BMSC) coculture model, ASARM peptides, anti-ASARM antibodies, and a small synthetic PHEX peptide (SPR4; 4.2 kDa) to examine this. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and two-dimensional (1)H/(15)N nuclear magnetic resonance demonstrated specific binding of SPR4 peptide to ASARM peptide. When cultured individually for 21 d, HYP BMSCs displayed reduced mineralization compared with wild type (WT) (-87%, P < 0.05). When cocultured, both HYP and WT cells failed to mineralize. However, cocultures (HYP and WT) or monocultures of HYP BMSCs treated with SPR4 peptide or anti-ASARM neutralizing antibodies mineralized normally. WT BMSCs treated with ASARM peptide also failed to mineralize properly without SPR4 peptide or anti-ASARM neutralizing antibodies. ASARM peptide treatment decreased PHEX mRNA and protein (-80%, P < 0.05) and SPR4 peptide cotreatment reversed this by binding ASARM peptide. SPR4 peptide also reversed ASARM peptide-mediated changes in expression of key osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation genes. Western blots of HYP calvariae and BMSCs revealed massive degradation of both MEPE and DMP1 protein compared with the WT. We conclude that degradation of MEPE and DMP-1 and release of ASARM peptides are chiefly responsible for the HYP mineralization defect and changes in osteoblast-osteoclast differentiation.
Figures

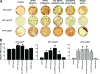



References
-
- Francis F, Hennig S, Korn B, Reinhardt R, de Jong D, Poustka A, Lehrach H, Rowe PS, Goulding JN, Summerfield T, Mountford RC, Read AP, Popowska E, Pronicka E, Davies KE, O’Riordan JL, Econs MJ, Nesbitt T, Drezner MK, Oudet C, Pannetier S, Hanauer A, Strom TM, Meindl A, Lorenz B, Cagnoli M, Mohnike KL, Murken J, Meitinger T 1995 A gene (PEX) with homologies to endopeptidases is mutated in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. The HYP Consortium. Nat Genet 11:130–136
-
- Prie D, Beck L, Urena P, Friedlander G 2005 Recent findings in phosphate homeostasis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 14:318–324 - PubMed
-
- Turner AJ, Tanzawa K 1997 Mammalian membrane metallopeptidases: NEP, ECE, KELL, and PEX. FASEB J 11:355–364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

