Nrf2 signaling: an adaptive response pathway for protection against environmental toxic insults
- PMID: 18164232
- PMCID: PMC2585047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2007.11.006
Nrf2 signaling: an adaptive response pathway for protection against environmental toxic insults
Abstract
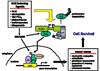
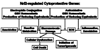
Human exposures to environmental toxicants have been associated with development of a number of diseases. Animal experiments have identified a number of cytoprotective enzymes under the transcriptional control of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) including electrophile conjugation and antioxidative enzymes and enzymes responsible for the production of antioxidants, reducing equivalents and cofactors. The up-regulation of these enzymes represents an adaptive response which occurs in the face of exposure to electrophilic or oxidative compounds thereby leading to enhanced metabolism of these molecules or their reactive metabolites. This adaptive response is regulated by an interaction between Keap1 and Nrf2 in which the exposure to reactive molecules is sensed either directly by Keap1 or indirectly by cellular signaling cascades resulting in activation of Nrf2 transcriptional regulation. The Nrf2-mediated adaptive response has been shown to attenuate toxicity and carcinogenesis during electrophile or oxidative stress as well as inflammation in rodent models. The cytoprotective attributes of the Nrf2 signaling pathway have been targeted for chemoprevention as administration of Nrf2-inducing agents has been shown to result in decreased carcinogenesis in animal models and altered carcinogen metabolism in humans. On the other hand, polymorphisms in the Nrf2 signaling pathway can lead to differential susceptibility to disease while mutations in the Nrf2 signaling pathway have been shown to an effective mechanism for cancer cells to evade chemotherapy. Overall, the Nrf2 cytoprotective adaptive response has evolved to be a powerful protective strategy for organisms against exposure to environmental toxicants and may provide insight into differential disease susceptibilities across populations and responses to therapies designed to alleviate these conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M. Molecular mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7:385–394. - PubMed
-
- Yu X, Kensler T. Nrf2 as a target for cancer chemoprevention. Mutat Res. 2005;591:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Kensler TW. The role of keap1 in cellular protective responses. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005;18:1779–1791. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases