N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)retinamide induced differentiation with repression of telomerase and cell cycle to increase interferon-gamma sensitivity for apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 18164543
- PMCID: PMC3103940
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.11.016
N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)retinamide induced differentiation with repression of telomerase and cell cycle to increase interferon-gamma sensitivity for apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells
Abstract
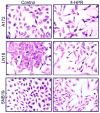
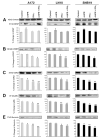
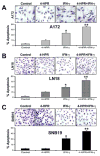
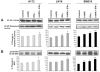
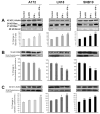
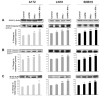
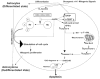
Glioblastoma is the most malignant and prevalent brain tumor in humans. It is composed of heterogenic abnormal astroglial cells that avoid differentiation, maintain proliferation, and hardly commit apoptosis. N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)retinamide (4-HPR) induced astrocytic differentiation and increased sensitivity to interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) for apoptosis in human glioblastoma A172, LN18, and SNB19 cells. Combination of 4-HPR and IFN-gamma significantly inhibited human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT), cyclin dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), and survivin to up-regulate caspase-8, caspase-9, and caspase-3 for increasing apoptosis in all glioblastoma cell lines. Hence, combination of 4-HPR and IFN-gamma should be considered for controlling growth of different human glioblastoma cells.
Figures
References
-
- Ray SK, Patel SJ, Welsh CT, Wilford GG, Hogan EL, Banik NL. Molecular evidence of apoptotic death in malignant brain tumors including glioblastoma multiforme: upregulation of calpain and caspase-3. J Neurosci Res. 2002;69:197–206. - PubMed
-
- Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Rorke LB, Reifenberger G, Burger PC, et al. The WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002;61:215–225. - PubMed
-
- Parney IF, Chang SM. Current chemotherapy for glioblastoma. Cancer J. 2003;9:149–156. - PubMed
-
- Parney IF, Hao C, Petruk KC. Glioblastoma immunology and immunotherapy. Neurosurgery. 2000;46:778–91. - PubMed
-
- Chambon PA. Decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996;10:940–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

