Experimental amniotic fluid infection in sheep: effects of Ureaplasma parvum serovars 3 and 6 on preterm or term fetal sheep
- PMID: 18166324
- PMCID: PMC2213425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.06.065
Experimental amniotic fluid infection in sheep: effects of Ureaplasma parvum serovars 3 and 6 on preterm or term fetal sheep
Abstract
Objective: The objective of the study was to determine the effects in late gestation of Ureaplasma parvum serovar 3 colonization and the effects, preterm, of U. parvum serovar 6.
Study design: Ewes received an intraamniotic (i.a.) injection of U. parvum serovar 6 (20 x 10(6) colony-forming units [cfu]; n = 9), U. parvum serovar 3 (20 x 10(3) cfu; n = 6), vehicle (n = 10), or saline (n = 4) on day 80 of pregnancy (d). The lambs were delivered at 125 d (U. parvum serovar 6, n = 9; saline or media controls, n = 9) or 145 d (U. parvum serovar 3, n = 6; media controls, n = 5) for assessment of inflammation and lung maturation.
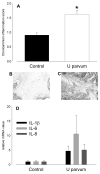
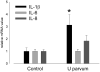
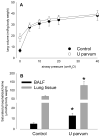
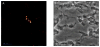
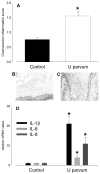
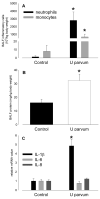
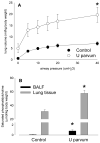
Results: I.a. ureaplasmas caused histologic chorioamnionitis but not preterm delivery. Fetal lung epithelium was colonized with ureaplasmas at both gestational ages, and pulmonary interleukin-8 levels had doubled in the ureaplasma-colonized animals, compared with the controls at 145 d. Surfactant levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid had increased 8-fold and 2.5-fold at 125 and 145 d, respectively, after ureaplasma injection.
Conclusion: Fetal lung inflammation and altered development accompanies ureaplasma colonization, regardless of age at delivery.
Figures


References
-
- Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC, Andrews WW. Intrauterine infection and preterm delivery. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1500–7. - PubMed
-
- Goncalves LF, Chaiworapongsa T, Romero R. Intrauterine infection and prematurity. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2002;8:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Witt A, Berger A, Gruber CJ, Petricevic L, Apfalter P, Worda C, Husslein P. Increased intrauterine frequency of Ureaplasma urealyticum in women with preterm labor and preterm premature rupture of the membranes and subsequent cesarean delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193:1663–9. - PubMed
-
- Kafetzis DA, Skevaki CL, Skouteri V, Gavrili S, Peppa K, Kostalos C, Petrochilou V, Michalas S. Maternal genital colonization with ureaplasma urealyticum promotes preterm delivery: association of the respiratory colonization of premature infants with chronic lung disease and increased mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1113–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

