Detection of a microbial biofilm in intraamniotic infection
- PMID: 18166328
- PMCID: PMC2614390
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.11.026
Detection of a microbial biofilm in intraamniotic infection
Abstract
Objective: Microbial biofilms are communities of sessile microorganisms formed by cells that are attached irreversibly to a substratum or interface or to each other and embedded in a hydrated matrix of extracellular polymeric substances. Microbial biofilms have been implicated in >80% of human infections such as periodontitis, urethritis, endocarditis, and device-associated infections. Thus far, intraamniotic infection has been attributed to planktonic (free-floating) bacteria. A case is presented in which "amniotic fluid sludge" was found to contain microbial biofilms. This represents the first report of a microbial biofilm in the amniotic cavity.
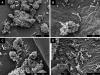
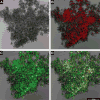
Study design: "Amniotic fluid sludge" was detected by transvaginal sonography and retrieved by transvaginal amniotomy. Bacteria were identified with scanning electron microscopy and fluorescence in situ hybridization for conserved regions of the microbial genome; the exopolymeric matrix was identified by histochemistry by the wheat germ agglutinin lectin method. The structure of the biofilm was imaged with confocal laser scanning microscopy.
Results: "Amniotic fluid sludge" was imaged with scanning electron microscopy, which allowed the identification of bacteria embedded in an amorphous material and inflammatory cells. Bacteria were demonstrated with fluorescent in situ hybridization using a eubacteria probe. Extracellular matrix was identified with the wheat germ agglutinin lectin stain. Confocal microscopy allowed 3-dimensional visualization of the microbial biofilm.
Conclusion: Microbial biofilms have been identified in a case of intraamniotic infection with "amniotic fluid sludge."
Figures



References
-
- Cassell GH, Davis RO, Waites KB, Brown MB, Marriott PA, Stagno S, et al. Isolation of Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma urealyticum from amniotic fluid at 16–20 weeks of gestation: potential effect on outcome of pregnancy. Sex Transm Dis. 1983;10:294–302. - PubMed
-
- Gray DJ, Robinson HB, Malone J, Thomson RB., Jr Adverse outcome in pregnancy following amniotic fluid isolation of Ureaplasma urealyticum. Prenat Diagn. 1992;12:111–17. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz S, Mazor M, Romero R, Horowitz J, Glezerman M. Infection of the amniotic cavity with Ureaplasma urealyticum in the midtrimester of pregnancy. J Reprod Med. 1995;40:375–79. - PubMed
-
- Gerber S, Vial Y, Hohlfeld P, Witkin SS. Detection of Ureaplasma urealyticum in second-trimester amniotic fluid by polymerase chain reaction correlates with subsequent preterm labor and delivery. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:518–21. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DP, Gerber S, Hohlfeld P, Sandrine G, Witkin SS. Mycoplasma hominis in mid-trimester amniotic fluid: relation to pregnancy outcome. J Perinat Med. 2004;32:323–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

