Involvement of protein kinase C beta-extracellular signal-regulating kinase 1/2/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-heat shock protein 27 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility and invasion
- PMID: 18167130
- PMCID: PMC11158944
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00702.x
Involvement of protein kinase C beta-extracellular signal-regulating kinase 1/2/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-heat shock protein 27 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility and invasion
Abstract
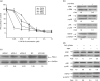
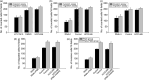
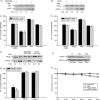
To understand the molecular mechanism that underlies the role of various prominent signal pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) metastasis, a human signal transduction oligonucleotide microarray analysis was carried out in cultured HCC cell models with increasing spontaneous metastatic potential (MHCC97L, MHCC97H, and HCCLM6). The results revealed that the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is the prominently upregulated pathway in HCC metastasis. Further study showed that basal phosphorylated levels of extracellular signal-regulating kinase (ERK)(1/2) and p38 MAPK consecutively increased from MHCC97L to MHCC97H to HCCLM6 cells, but not c-Jun N-terminal kinase. The phosphorylation of ERK(1/2) and p38 MAPK was regulated by upregulated protein kinase C beta (PKC beta) in HCC cells through the integrated use of PKC beta RNA interference, the PKC beta specific inhibitor enzastaurin and a PKC activator phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate. Heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) was also verified as a downstream common activated protein of PKC beta-ERK(1/2) and PKC beta-p38 MAPK. In vitro migration and invasion assay further showed that the depletion of PKC beta or inhibition of PKC beta activation effectively decreased HCC cell motility and invasion. Moreover, the motility and invasion of phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-stimulated PKC beta-mediated HCC cells was significantly negated by an ERK inhibitor, 1.4-diamino-2.3-dicyano-1.4-bis[2-aminophenylthio] butadiene, or a p38 MAPK inhibitor, 4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-(4-methylsulfinylphenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)1H-imidazole. It also showed that HSP27 is critical in PKC beta-mediated HCC cell motility and invasion. Taken together, this study reveals the important role of this PKC beta-ERK(1/2)/p38MAPK-HSP27 pathway, which was verified for the first time, in modulating HCC cell motility and invasion.
Figures



Similar articles
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in protein kinase Calpha-regulated invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cancer Res. 2007 May 1;67(9):4320-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2486. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17483345
-
Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in heat shock protein 27 induction in human neutrophils.Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Apr 18;466(3):245-53. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01571-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12694807
-
Regulation of HSP27 on NF-kappaB pathway activation may be involved in metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cells apoptosis.BMC Cancer. 2009 Mar 31;9:100. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-100. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19331697 Free PMC article.
-
Progress of Pyruvate Kinase M2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Associated Signaling Pathway.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2025 Mar;31(3):101-107. doi: 10.1089/ten.tec.2024.0368. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2025. PMID: 40105913 Review.
-
Role of p38 MAP kinase in cancer stem cells and metastasis.Oncogene. 2022 Jun;41(23):3177-3185. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02329-3. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35501462 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic research progress in lymphatic metastases of cancers.Clin Transl Oncol. 2012 Jan;14(1):21-30. doi: 10.1007/s12094-012-0757-7. Clin Transl Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22262715 Review.
-
Targeting Ser78 phosphorylation of Hsp27 achieves potent antiviral effects against enterovirus A71 infection.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2368221. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2368221. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38932432 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of key pathways in sorafenib-treated hepatocellular carcinoma based on a PCR-array.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Mar 1;8(3):3027-35. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26045814 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of enzastaurin and pemetrexed inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis of chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells regulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation.Transl Oncol. 2009 Aug 18;2(3):164-73. doi: 10.1593/tlo.09121. Transl Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19701501 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine prevents non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-derived hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting inflammation and angiogenesis in mice.Am J Transl Res. 2019 May 15;11(5):2668-2682. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31217846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Budhu AS, Zipser B, Forgues M, Ye QH, Sun Z, Wang XW. The molecular signature of metastases of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2005; 69: 23–7. - PubMed
-
- Chambers AF, MacDonald IC, Schmidt EE, Morris VL, Groom AC. Clinical targets for anti‐metastasis therapy. Adv Cancer Res 2000; 79: 91–121. - PubMed
-
- Tang ZY. Hepatocellular carcinoma surgery – review of the past and prospects for the 21st century. J Surg Oncol 2005; 91: 95–6. - PubMed
-
- Christofori G. New signals from the invasive front. Nature 2006; 441: 444–50. - PubMed
-
- Wieser R. The transforming growth factor‐beta signaling pathway in tumorigenesis. Curr Opin Oncol 2001; 13: 70–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

