RNAi screens reveal novel metabolic regulators: RIP140, MAP4k4 and the lipid droplet associated fat specific protein (FSP) 27
- PMID: 18171433
- PMCID: PMC2880506
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01786.x
RNAi screens reveal novel metabolic regulators: RIP140, MAP4k4 and the lipid droplet associated fat specific protein (FSP) 27
Abstract
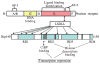
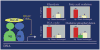
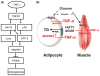
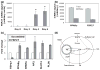
Adipose tissue modulates whole body metabolism and insulin sensitivity by controlling circulating lipid levels and producing molecules that can regulate fatty acid metabolism in such tissues as muscle and liver. We have developed RNA interference (RNAi) screens to identify genes in cultured adipocytes that regulate insulin signalling and key metabolic pathways. These short interfering RNA (siRNA)-based screens identified the transcriptional corepressor receptor interacting protein 140 (RIP140) (J Clin Invest 116: 125, 2006) and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP4k4) (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 2087, 2006) as negative regulators of insulin-responsive hexose uptake and oxidative metabolism. Gene expression profiling revealed that RIP140 depletion upregulates the expression of clusters of genes in the pathways of glucose uptake, glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle, fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative phosphorylation. RIP140-null mice resist weight gain on a high-fat diet and display enhanced glucose tolerance. MAP4k4 depletion in adipocytes increases many of the RIP140-sensitive genes, increases adipogenesis and mediates some actions of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Remarkably, another hit in our RNAi screens was fat specific protein 27 (FSP27), a highly expressed isoform of Cidea. We discovered that FSP27 unexpectedly associates specifically with lipid droplets and regulates fat storage. We conclude that RIP140, MAP4k4 and the novel lipid droplet protein FSP27 are powerful regulators of adipose tissue metabolism and are potential therapeutic targets for controlling metabolic disease. The discovery of these novel proteins validates the power of RNAi screening for discovery of new therapeutic approaches to type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
M.P.C. and A.G. own, or may be provided, equity in CytRx, Inc., based on intellectual property licensed from the University of Massachusetts Medical School, which shares royalties with inventors.
Figures


References
-
- Ahren B. Type 2 diabetes, insulin secretion and beta-cell mass. Curr Mol Med. 2005;5:275–286. - PubMed
-
- Augereau P, Badia E, Fuentes M, Rabenoelina F, Corniou M, Derocq D, Balaguer P, Cavailles V. Transcriptional regulation of the human NRIP1/RIP140 gene by estrogen is modulated by dioxin signalling. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;69:1338–1346. - PubMed
-
- Bouzakri K, Zierath JR. MAP4K4 gene silencing in human skeletal muscle prevents tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:7783–7789. - PubMed
-
- Brasaemle DL, Dolios G, Shapiro L, Wang R. Proteomic analysis of proteins associated with lipid droplets of basal and lipolytically stimulated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:46835–46842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

