Enhanced excitation-coupled calcium entry in myotubes expressing malignant hyperthermia mutation R163C is attenuated by dantrolene
- PMID: 18171728
- PMCID: PMC2735873
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.107.043299
Enhanced excitation-coupled calcium entry in myotubes expressing malignant hyperthermia mutation R163C is attenuated by dantrolene
Abstract
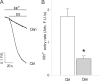
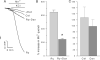
Dantrolene is the drug of choice for the treatment of malignant hyperthermia (MH) and is also useful for treatment of spasticity or muscle spasms associated with several clinical conditions. The current study examines the mechanisms of dantrolene's action on skeletal muscle and shows that one of dantrolene's mechanisms of action is to block excitation-coupled calcium entry (ECCE) in both adult mouse flexor digitorum brevis fibers and primary myotubes. A second important new finding is that myotubes isolated from mice heterozygous and homozygous for the ryanodine receptor type 1 R163C MH susceptibility mutation show significantly enhanced ECCE rates that could be restored to those measured in wild-type cells after exposure to clinical concentrations of dantrolene. We propose that this gain of ECCE function is an important etiological component of MH susceptibility and possibly contributes to the fulminant MH episode. The inhibitory potency of dantrolene on ECCE found in wild-type and MH-susceptible muscle is consistent with the drug's clinical potency for reversing the MH syndrome and is incomplete as predicted by its efficacy as a muscle relaxant.
Figures






References
-
- Ali SZ, Taguchi A, Rosenberg H. Malignant hyperthermia. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2003;17:519–533. - PubMed
-
- Bidasee KR, Xu L, Meissner G, Besch HR., Jr Diketopyridylryanodine has three concentration-dependent effects on the cardiac calcium-release channel/ ryanodine receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:14237–14248. - PubMed
-
- Bjurström SCJ, Jönsson L. The reduction of skeletal muscle lesions after experimental stress in stress-susceptible pigs protected with dantrolene. Zentralbl Veterinar Med A. 1995;42:659–667. - PubMed
-
- Buck ED, Nguyen HT, Pessah IN, Allen PD. Dyspedic mouse skeletal muscle expresses major elements of the triadic junction but lacks detectable ryanodine receptor protein and function. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:7360–7367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

