HIV-protease inhibitors induce expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 in insulin-sensitive tissues and promote insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 18171911
- PMCID: PMC3711823
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00167.2007
HIV-protease inhibitors induce expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 in insulin-sensitive tissues and promote insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
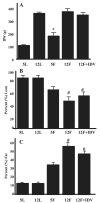
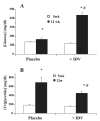
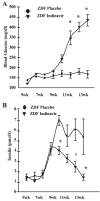
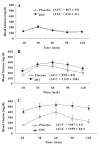
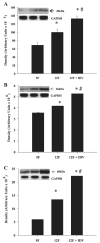
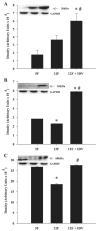
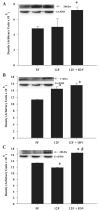
Insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and type 2 diabetes are among the sequelae of metabolic syndromes that occur in 60-80% of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive patients treated with HIV-protease inhibitors (PIs). Studies to elucidate the molecular mechanism(s) contributing to these changes, however, have mainly focused on acute, in vitro actions of PIs. Here, we examined the chronic (7 wk) in vivo effects of the PI indinavir (IDV) in male Zucker diabetic fatty (fa/fa) (ZDF) rats. IDV exposure accelerated the diabetic state and dramatically exacerbated hyperglycemia and oral glucose intolerance in the ZDF rats, compared with vehicle-treated ZDF rats. Oligonucleotide gene array analyses revealed upregulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS-1) expression in insulin-sensitive tissues of IDV rats. SOCS-1 is a known inducer of insulin resistance and diabetes, and immunoblotting analyses revealed increases in SOCS-1 protein expression in adipose, skeletal muscle, and liver tissues of IDV-administered ZDF rats. This was associated with increases in the upstream regulator TNF-alpha and downstream effector sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 and a decrease in IRS-2. IDV and other PIs currently in clinical use induced the SOCS-1 signaling cascade also in L6 myotubes and 3T3-L1 adipocytes exposed acutely to PIs under normal culturing conditions and in tissues from Zucker wild-type lean control rats administered PIs for 3 wk, suggesting an effect of these drugs even in the absence of background hyperglycemia/hyperlipidemia. Our findings therefore indicate that induction of the SOCS-1 signaling cascade by PIs could be an important contributing factor in the development of metabolic dysregulation associated with long-term exposures to HIV-PIs.
Figures
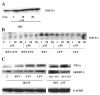
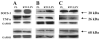
References
-
- Abel ED, Peroni O, Kim JK, Kim YB, Boss O, Hadro E, Minnemann T, Shulman GI, Kahn BB. Adipose-selective targeting of the GLUT4 gene impairs insulin action in muscle and liver. Nature. 2001;409:729–733. - PubMed
-
- Alexander WS, Hilton DJ. The role of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in regulation of the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:503–529. - PubMed
-
- Almind K, Doria A, Kahn CR. Putting the genes for type II diabetes on the map. Nat Med. 2001;7:277–279. - PubMed
-
- Autran B, Carcelain G, Li TS, Blanc C, Mathez D, Tubiana R, Katlama C, Debre P, Leibowitch J. Positive effects of combined anti-retroviral therapy on CD4+ T cell homeostasis and function in advanced HIV disease. Science. 1997;277:112–116. - PubMed
-
- Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, Capeau J, Feve B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006;17:4–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P60-DK-020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-074345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-69455/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-049393/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-056431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK074343/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK049393/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007296/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P41-RR00954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069455/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-059531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049393/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK074345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DK-007296-27/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK-074343/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

