Inhibition of serotonin but not norepinephrine transport during development produces delayed, persistent perturbations of emotional behaviors in mice
- PMID: 18171937
- PMCID: PMC6671162
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3973-07.2008
Inhibition of serotonin but not norepinephrine transport during development produces delayed, persistent perturbations of emotional behaviors in mice
Abstract
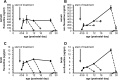
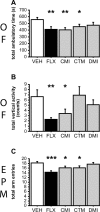
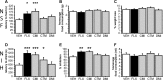
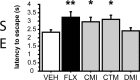
Serotonin (5-HT) acts as a neurotransmitter, but also modulates brain maturation during early development. The demonstrated influence of genetic variants on brain function, personality traits, and susceptibility to neuropsychiatric disorders suggests a critical importance of developmental mechanisms. However, little is known about how and when developmentally perturbed 5-HT signaling affects circuitry and resulting behavior. The 5-HT transporter (5-HTT) is a key regulator of extracellular 5-HT levels and we used pharmacologic strategies to manipulate 5-HTT function during development and determine behavioral consequences. Transient exposure to the 5-HTT inhibitors fluoxetine, clomipramine, and citalopram from postnatal day 4 (P4) to P21 produced abnormal emotional behaviors in adult mice. Similar treatment with the norepinephrine transporter (NET) inhibitor, desipramine, did not adversely affect adult behavior, suggesting that 5-HT and norepinephrine (NE) do not share the same effects on brain development. Shifting our period of treatment/testing to P90/P185 failed to mimic the effect of earlier exposure, demonstrating that 5-HT effects on adult behavior are developmentally specific. We have hypothesized that early-life perturbations of 5-HT signaling affect corticolimbic circuits that do not reach maturity until the peri-adolescent period. In support of this idea, we found that abnormal behaviors resulting from postnatal fluoxetine exposure have a post-pubescent onset and persist long after reaching adult age. A better understanding of the underlying 5-HT sensitive circuits and how they are perturbed should lead to new insights into how various genetic polymorphisms confer their risk to carriers. Furthermore, these studies should help determine whether in utero exposure to 5-HTT blocking drugs poses a risk for behavioral abnormalities in later life.
Figures
References
-
- Ansorge MS, Zhou M, Lira A, Hen R, Gingrich JA. Early-life blockade of the 5-HT transporter alters emotional behavior in adult mice. Science. 2004;306:879–881. - PubMed
-
- Ansorge MS, Hen R, Gingrich JA. Neurodevelopmental origins of depressive disorders. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007;7:8–17. - PubMed
-
- Argenti D, D'Mello AP. The pharmacodynamics of desipramine and desmethyldesipramine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;270:512–519. - PubMed
-
- Balant-Gorgia AE, Gex-Fabry M, Balant LP. Clinical pharmacokinetics of clomipramine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991;20:447–462. - PubMed
-
- Barr CS, Newman TK, Schwandt M, Shannon C, Dvoskin RL, Lindell SG, Taubman J, Thompson B, Champoux M, Lesch KP, Goldman D, Suomi SJ, Higley JD. Sexual dichotomy of an interaction between early adversity and the serotonin transporter gene promoter variant in rhesus macaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:12358–12363. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
