Testosterone-induced matrix metalloproteinase activation is a checkpoint for neuronal addition to the adult songbird brain
- PMID: 18171938
- PMCID: PMC6671156
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3674-07.2008
Testosterone-induced matrix metalloproteinase activation is a checkpoint for neuronal addition to the adult songbird brain
Abstract
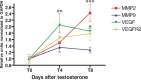
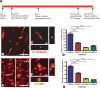
Testosterone-induced neuronal addition to the adult songbird vocal control center, HVC, requires the androgenic induction of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), followed by VEGF-stimulated angiogenesis. The expanded vasculature acts as a source of BDNF, which supports the immigration of new neurons from the overlying ventricular zone. In tumorigenesis, a similar process of adult angiogenesis is regulated by matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity, in particular that of the gelatinases. We therefore investigated the role of the gelatinases in neuronal addition to the HVC of adult female canaries. In situ zymography of the caudal forebrain revealed that testosterone-induced perivascular gelatinase activity that was most prominent in HVC. High-resolution gels revealed distinct MMP activities that comigrated with MMP2 and MMP9, and PCR cloning yielded MMP2 and MMP9 orthologues of 1465 and 1044 bp, respectively. Quantitative PCR revealed that HVC MMP2 mRNA levels doubled within 8 d of testosterone, whereas MMP9 transcript levels were stable. Moreover, isolated adult canary forebrain endothelial cells secreted MMP2, and VEGF substantially increased endothelial MMP2 gelatinase activity. To assess the importance of androgen-regulated, VEGF-induced MMP2 to adult angiogenesis and neurogenesis, we treated testosterone-implanted females with the gelatinase inhibitor SB-3CT. In situ zymography confirmed that SB-3CT suppressed gelatinase activity in HVC, and histological analysis revealed that SB-3CT-treated birds exhibited a decreased endothelial mitotic index and substantially diminished neuronal recruitment to HVC. These data suggest that the androgenic induction of endothelial MMP2 is a critical regulator of neuronal addition to the adult HVC, and as such comprises an important regulatory step in adult neurogenesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Coordinated interaction of neurogenesis and angiogenesis in the adult songbird brain.Neuron. 2002 Jun 13;34(6):945-60. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00722-5. Neuron. 2002. PMID: 12086642
-
Testosterone modulation of angiogenesis and neurogenesis in the adult songbird brain.Neuroscience. 2013 Jun 3;239:139-48. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.043. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23291451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MMP2 and MMP9-specific inhibitor SB-3CT significantly decreases blood pressure in pre-eclampsia model rats.Biol Reprod. 2025 Jul 13;113(1):209-219. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioaf075. Biol Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40159316
-
Neuronal production, migration, and differentiation in a vocal control nucleus of the adult female canary brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2390-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2390. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983. PMID: 6572982 Free PMC article.
-
Birth, migration, incorporation, and death of vocal control neurons in adult songbirds.J Neurobiol. 1997 Nov;33(5):585-601. J Neurobiol. 1997. PMID: 9369461 Review.
Cited by
-
In ovo administration of human recombinant leptin shows dose dependent angiogenic effect on chicken chorioallantoic membrane.Biol Res. 2015 Jun 10;48(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40659-015-0021-z. Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 26060038 Free PMC article.
-
Perivascular instruction of cell genesis and fate in the adult brain.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Oct 26;14(11):1382-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.2963. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22030549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-9 regulates basal ganglia-dependent developmental vocal learning and adult vocal performance in songbirds.Elife. 2018 Jan 18;7:e29087. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29087. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29345619 Free PMC article.
-
A New Signaling Pathway for HCV Inhibition by Estrogen: GPR30 Activation Leads to Cleavage of Occludin by MMP-9.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):e0145212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145212. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26731262 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen induced cellular proliferation, neurogenesis, and generation of GnRH3 neurons in the brain of mature female Mozambique tilapia.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 15;8(1):16855. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35303-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30442908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A. Neurogenesis and plasticity in the CNS of adult birds. Exp Neurol. 1992;115:110–114. - PubMed
-
- Barami K, Iverson K, Furneaux H, Goldman P. Early expression of Hu proteins by newly generated neurons in the adult avian forebrain. J Neurobiol. 1995;28:82–101. - PubMed
-
- Barami K, Kirschenbaum B, Lemmon V, Goldman SA. N-cadherin and Ng-CAM/8D9 are involved serially in the migration of newly generated neurons into the adult songbird brain. Neuron. 1994;13:567–582. - PubMed
-
- Brown S, Bernardo M, Li Z, Kotra L, Tanaka Y, Fridman R, Mobashery S. Potent and selective mechanism-based inhibition of gelatinases. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:6799–6800.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
