Regulation of MDMX expression by mitogenic signaling
- PMID: 18172009
- PMCID: PMC2268405
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01633-07
Regulation of MDMX expression by mitogenic signaling
Abstract
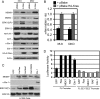
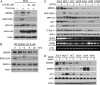
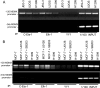
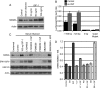
MDMX is an important regulator of p53 transcriptional activity and stress response. MDMX overexpression and gene amplification are implicated in p53 inactivation and tumor development. Unlike MDM2, MDMX is not inducible by p53, and little is known about its regulation at the transcriptional level. We found that MDMX levels in tumor cell lines closely correlate with promoter activity and mRNA level. Activated K-Ras and insulin-like growth factor 1 induce MDMX expression at the transcriptional level through mechanisms that involve the mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Ets-1 transcription factors. Pharmacological inhibition of MEK results in down-regulation of MDMX in tumor cell lines. MDMX overexpression was detected in approximately 50% of human colon tumors and showed strong correlation with increased extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation. Therefore, MDMX expression is regulated by mitogenic signaling pathways. This mechanism may protect normal proliferating cells from p53 but also hamper p53 response during tumor development.
Figures




References
-
- Agarwal, M. L., C. V. Ramana, M. Hamilton, W. R. Taylor, S. E. DePrimo, L. J. Bean, A. Agarwal, M. K. Agarwal, A. Wolfman, and G. R. Stark. 2001. Regulation of p53 expression by the RAS-MAP kinase pathway. Oncogene 202527-2536. - PubMed
-
- Banin, S., L. Moyal, S. Shieh, Y. Taya, C. W. Anderson, L. Chessa, N. I. Smorodinsky, C. Prives, Y. Reiss, Y. Shiloh, and Y. Ziv. 1998. Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science 2811674-1677. - PubMed
-
- Bond, G. L., W. Hu, E. E. Bond, H. Robins, S. G. Lutzker, N. C. Arva, J. Bargonetti, F. Bartel, H. Taubert, P. Wuerl, K. Onel, L. Yip, S. J. Hwang, L. C. Strong, G. Lozano, and A. J. Levine. 2004. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2 promoter attenuates the p53 tumor suppressor pathway and accelerates tumor formation in humans. Cell 119591-602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
