Alpha-synuclein-induced aggregation of cytoplasmic vesicles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 18172022
- PMCID: PMC2262993
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-08-0827
Alpha-synuclein-induced aggregation of cytoplasmic vesicles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Erratum in
- Mol Biol Cell. 2008 May;19(5):2348
Abstract
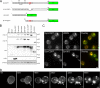
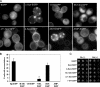
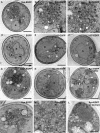
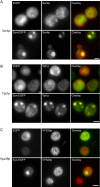
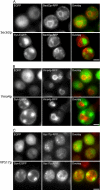
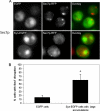
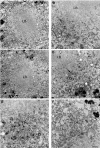
Aggregated alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) fibrils form Lewy bodies (LBs), the signature lesions of Parkinson's disease (PD) and related synucleinopathies, but the pathogenesis and neurodegenerative effects of LBs remain enigmatic. Recent studies have shown that when overexpressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, alpha-syn localizes to plasma membranes and forms cytoplasmic accumulations similar to human alpha-syn inclusions. However, the exact nature, composition, temporal evolution, and underlying mechanisms of yeast alpha-syn accumulations and their relevance to human synucleinopathies are unknown. Here we provide ultrastructural evidence that alpha-syn accumulations are not comprised of LB-like fibrils, but are associated with clusters of vesicles. Live-cell imaging showed alpha-syn initially localized to the plasma membrane and subsequently formed accumulations in association with vesicles. Imaging of truncated and mutant forms of alpha-syn revealed the molecular determinants and vesicular trafficking pathways underlying this pathological process. Because vesicular clustering is also found in LB-containing neurons of PD brains, alpha-syn-mediated vesicular accumulation in yeast represents a model system to study specific aspects of neurodegeneration in PD and related synucleinopathies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Parkinson's disease protein alpha-synuclein disrupts cellular Rab homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jan 8;105(1):145-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710685105. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18162536 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils seed the formation of Lewy body-like intracellular inclusions in cultured cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 24;106(47):20051-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908005106. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19892735 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Synuclein and the Endolysosomal System in Parkinson's Disease: Guilty by Association.Biomolecules. 2021 Sep 9;11(9):1333. doi: 10.3390/biom11091333. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34572546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteration of Structure and Aggregation of α-Synuclein by Familial Parkinson's Disease Associated Mutations.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(7):656-676. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160314151706. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 26972727 Review.
-
Alpha-synuclein blocks ER-Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson's models.Science. 2006 Jul 21;313(5785):324-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1129462. Epub 2006 Jun 22. Science. 2006. PMID: 16794039 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
From Synaptic Physiology to Synaptic Pathology: The Enigma of α-Synuclein.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 12;25(2):986. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020986. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Yeast to Humans: Leveraging New Approaches in Yeast to Accelerate Discovery of Therapeutic Targets for Synucleinopathies.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2049:419-444. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9736-7_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31602625
-
Parallel mechanisms for direct and indirect membrane protein trafficking by synucleins.Commun Integr Biol. 2013 Nov 1;6(6):e26794. doi: 10.4161/cib.26794. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Commun Integr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24563712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Rescue α-Synuclein-Induced Toxicity in a Yeast Model of Parkinson's Disease.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jan 29;10(2):235. doi: 10.3390/nano10020235. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32013138 Free PMC article.
-
Direct membrane association drives mitochondrial fission by the Parkinson disease-associated protein alpha-synuclein.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 10;286(23):20710-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.213538. Epub 2011 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21489994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abeliovich A., et al. Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron. 2000;25:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Chandra S., Gallardo G., Fernandez-Chacon R., Schluter O. M., Sudhof T. C. Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell. 2005;123:383–396. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Harlin M. C., et al. Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2004;364:1167–1169. - PubMed
-
- Cole N. B., Murphy D. D., Grider T., Rueter S., Brasaemle D., Nussbaum R. L. Lipid droplet binding and oligomerization properties of the Parkinson's disease protein alpha-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:6344–6352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

