Ypi1, a positive regulator of nuclear protein phosphatase type 1 activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 18172024
- PMCID: PMC2262978
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0499
Ypi1, a positive regulator of nuclear protein phosphatase type 1 activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
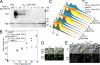
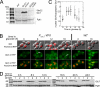
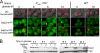
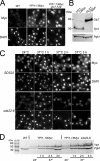
The catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase type 1 (PP1) has an essential role in mitosis, acting in opposition to the Ipl1/Aurora B protein kinase to ensure proper kinetochore-microtubule interactions. However, the regulatory subunit(s) that completes the PP1 holoenzyme that functions in this capacity is not known. We show here that the budding yeast Ypi1 protein is a nuclear protein that functions with PP1 (Glc7) in this mitotic role. Depletion of cellular Ypi1 induces mitotic arrest due to activation of the spindle checkpoint. Ypi1 depletion is accompanied by a reduction of nuclear PP1 and by loss of nuclear Sds22, a Glc7 binding partner that is found in a ternary complex with Ypi1 and Glc7. Expression of a Ypi1 variant that binds weakly to PP1 also activates the spindle checkpoint and suppresses the temperature sensitivity of an ipl1-2 mutant. These results, together with genetic interactions among YPI1, GLC7, and SDS22 mutants, indicate that Ypi1 and Sds22 are positive regulators of the nuclear Glc7 activity that is required for mitosis.
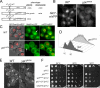
Figures


References
-
- Alessi D. R., Street A. J., Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Inhibitor-2 functions like a chaperone to fold three expressed isoforms of mammalian protein phosphatase-1 into a conformation with the specificity and regulatory properties of the native enzyme. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993;213:1055–1066. - PubMed
-
- Andrews P. D., Stark M. J. Type 1 protein phosphatase is required for maintenance of cell wall integrity, morphogenesis and cell cycle progression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Sci. 2000;113:507–520. - PubMed
-
- Axton J. M., Dombradi V., Cohen P.T.W., Glover D. M. One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell. 1990;63:33–46. - PubMed
-
- Black S., Andrews P. D., Sneddon A. A., Stark M. J. A regulated MET3-GLC7 gene fusion provides evidence of a mitotic role for Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase 1. Yeast. 1995;11:747–759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

