Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Golgi phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase Pik1 is regulated by 14-3-3 proteins and coordinates Golgi function with cell growth
- PMID: 18172025
- PMCID: PMC2262966
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0134
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Golgi phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase Pik1 is regulated by 14-3-3 proteins and coordinates Golgi function with cell growth
Abstract
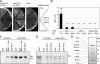
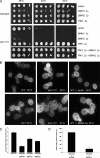
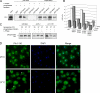
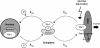
The yeast phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase Pik1p is essential for proliferation, and it controls Golgi homeostasis and transport of newly synthesized proteins from this compartment. At the Golgi, phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate recruits multiple cytosolic effectors involved in formation of post-Golgi transport vesicles. A second pool of catalytically active Pik1p localizes to the nucleus. The physiological significance and regulation of this dual localization of the lipid kinase remains unknown. Here, we show that Pik1p binds to the redundant 14-3-3 proteins Bmh1p and Bmh2p. We provide evidence that nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Pik1p involves phosphorylation and that 14-3-3 proteins bind Pik1p in the cytoplasm. Nutrient deprivation results in relocation of Pik1p from the Golgi to the nucleus and increases the amount of Pik1p-14-3-3 complex, a process reversed upon restored nutrient supply. These data suggest a role of Pik1p nucleocytoplasmic shuttling in coordination of biosynthetic transport from the Golgi with nutrient signaling.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Synthetic genetic array analysis of the PtdIns 4-kinase Pik1p identifies components in a Golgi-specific Ypt31/rab-GTPase signaling pathway.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):776-93. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-08-0700. Epub 2004 Dec 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15574876 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast phosphatidylinositol-4-OH kinase pik1 regulates secretion at the Golgi.Nat Cell Biol. 1999 Dec;1(8):523-5. doi: 10.1038/70319. Nat Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10587649 No abstract available.
-
Growth control of Golgi phosphoinositides by reciprocal localization of sac1 lipid phosphatase and pik1 4-kinase.Traffic. 2007 Nov;8(11):1554-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00632.x. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Traffic. 2007. PMID: 17908202
-
Surprising roles for phospholipid binding proteins revealed by high throughput genetics.Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;88(4):565-74. doi: 10.1139/O09-171. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20651827 Review.
-
Coordination of Golgi functions by phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases.Trends Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;21(2):113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Trends Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21282087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatic and experimental survey of 14-3-3-binding sites.Biochem J. 2010 Mar 15;427(1):69-78. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091834. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20141511 Free PMC article.
-
Function and dysfunction of the PI system in membrane trafficking.EMBO J. 2008 Oct 8;27(19):2457-70. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.169. Epub 2008 Sep 11. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18784754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The yeast arrestin-related protein Bul1 is a novel actor of glucose-induced endocytosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 May 1;29(9):1012-1020. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-07-0466. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29514933 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role for Schizosaccharomyces pombe pik1 in septation.PLoS One. 2009 Jul 9;4(7):e6179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006179. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19587793 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose regulates clathrin adaptors at the trans-Golgi network and endosomes.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Oct;22(19):3671-83. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0309. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21832155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ames J. B., Hendricks K. B., Strahl T., Huttner I. G., Hamasaki N., Thorner J. Structure and calcium-binding properties of Frq1, a novel calcium sensor in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 2000;39:12149–12161. - PubMed
-
- Bauer P. J., Krause E. Accessibility of cysteines in the native bovine rod cGMP-gated channel. Biochemistry. 2005;44:1624–1634. - PubMed
-
- Beck T., Hall M. N. The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient-regulated transcription factors. Nature. 1999;402:689–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

