A single Hox locus in Drosophila produces functional microRNAs from opposite DNA strands
- PMID: 18172160
- PMCID: PMC2151017
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1613108
A single Hox locus in Drosophila produces functional microRNAs from opposite DNA strands
Abstract
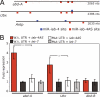
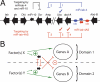
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are approximately 22-nucleotide RNAs that are processed from characteristic precursor hairpins and pair to sites in messages of protein-coding genes to direct post-transcriptional repression. Here, we report that the miRNA iab-4 locus in the Drosophila Hox cluster is transcribed convergently from both DNA strands, giving rise to two distinct functional miRNAs. Both sense and antisense miRNA products target neighboring Hox genes via highly conserved sites, leading to homeotic transformations when ectopically expressed. We also report sense/antisense miRNAs in mouse and find antisense transcripts close to many miRNAs in both flies and mammals, suggesting that additional sense/antisense pairs exist.
Figures

References
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Boulet A.M., Lloyd A., Sakonju S. Molecular definition of the morphogenetic and regulatory functions and the cis-regulatory elements of the Drosophila Abd-B homeotic gene. Development. 1991;111:393–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
