Photolysis of a caged peptide reveals rapid action of N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor before neurotransmitter release
- PMID: 18172208
- PMCID: PMC2224215
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0707197105
Photolysis of a caged peptide reveals rapid action of N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor before neurotransmitter release
Abstract
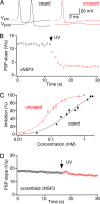
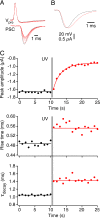
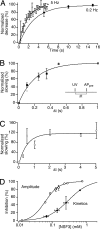
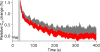
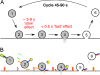
The time at which the N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) acts during synaptic vesicle (SV) trafficking was identified by time-controlled perturbation of NSF function with a photoactivatable inhibitory peptide. Photolysis of this caged peptide in the squid giant presynaptic terminal caused an abrupt (0.2 s) slowing of the kinetics of the postsynaptic current (PSC) and a more gradual (2-3 s) reduction in PSC amplitude. Based on the rapid rate of these inhibitory effects relative to the speed of SV recycling, we conclude that NSF functions in reactions that immediately precede neurotransmitter release. Our results indicate the locus of SNARE protein recycling in presynaptic terminals and reveal NSF as a potential target for rapid regulation of transmitter release.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of neurotransmitter release kinetics by NSF.Science. 1998 Feb 20;279(5354):1203-6. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5354.1203. Science. 1998. PMID: 9469810
-
Genetic analysis of soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein function in Drosophila reveals positive and negative secretory roles.J Neurosci. 2004 Apr 21;24(16):3964-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5259-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15102912 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium released by photolysis of DM-nitrophen stimulates transmitter release at squid giant synapse.J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:473-98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018150. J Physiol. 1990. PMID: 1977904 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotransmitter release - four years of SNARE complexes.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1997 Jun;7(3):310-5. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(97)80057-8. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1997. PMID: 9232812 Review.
-
Protein interactions implicated in neurotransmitter release.J Physiol Paris. 1998 Apr;92(2):129-33. doi: 10.1016/S0928-4257(98)80150-2. J Physiol Paris. 1998. PMID: 9782456 Review.
Cited by
-
A multivesicular body-like organelle mediates stimulus-regulated trafficking of olfactory ciliary transduction proteins.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 12;13(1):6889. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34604-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36371422 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms determining conserved properties of short-term synaptic depression revealed in NSF and SNAP-25 conditional mutants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 25;106(34):14658-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907144106. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19706552 Free PMC article.
-
Requirements for the catalytic cycle of the N-ethylmaleimide-Sensitive Factor (NSF).Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1823(1):159-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21689688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organization of a functional glycolytic metabolon on mitochondria for metabolic efficiency.Nat Metab. 2024 Sep;6(9):1712-1735. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01121-9. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Nat Metab. 2024. PMID: 39261628
-
Vesicle priming in a SNAP.Neuron. 2010 Nov 4;68(3):324-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.10.022. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 21040835 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

