Small animal imaging with magnetic resonance microscopy
- PMID: 18172332
- PMCID: PMC2770253
- DOI: 10.1093/ilar.49.1.35
Small animal imaging with magnetic resonance microscopy
Abstract
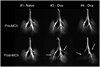
Small animal magnetic resonance microscopy (MRM) has evolved significantly from testing the boundaries of imaging physics to its expanding use today as a tool in noninvasive biomedical investigations. MRM now increasingly provides functional information about living animals, with images of the beating heart, breathing lung, and functioning brain. Unlike clinical MRI, where the focus is on diagnosis, MRM is used to reveal fundamental biology or to noninvasively measure subtle changes in the structure or function of organs during disease progression or in response to experimental therapies. High-resolution anatomical imaging reveals increasingly exquisite detail in healthy animals and subtle architectural aberrations that occur in genetically altered models. Resolution of 100 mum in all dimensions is now routinely attained in living animals, and (10 mum)(3) is feasible in fixed specimens. Such images almost rival conventional histology while allowing the object to be viewed interactively in any plane. In this review we describe the state of the art in MRM for scientists who may be unfamiliar with this modality but who want to apply its capabilities to their research. We include a brief review of MR concepts and methods of animal handling and support, before covering a range of MRM applications-including the heart, lung, and brain-and the emerging field of MR histology. The ability of MRM to provide a detailed functional and anatomical picture in rats and mice, and to track this picture over time, makes it a promising platform with broad applications in biomedical research.
Figures




References
-
- Ahrens ET, Dubowitz DJ. Peripheral somatosensory fMRI in mouse at 11.7 T. NMR Biomed. 2001;14:318–324. - PubMed
-
- Ali AA, Dale AM, Badea A, Johnson GA. Automated segmentation of neuroanatomical structures in multispectral MR microscopy of the mouse brain. Neuroimage. 2005;27:425–435. - PubMed
-
- Altes TA, Powers PL, Knight-Scott J, Rakes G, Platts-Mills TAE, DeLange EE, Alford BA, Mugler JP, Brookeman JR. Hyperpolarized 3He MR Lung Ventilation Imaging in Asthmatics: Preliminary Findings. J. Mag. Res. Imag. 2001;13:378–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

