Dopamine-modified alpha-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated autophagy
- PMID: 18172548
- PMCID: PMC2157565
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32806
Dopamine-modified alpha-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated autophagy
Abstract
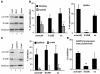
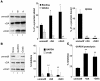
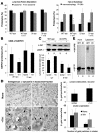
Altered degradation of alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease (PD). We have shown that alpha-syn can be degraded via chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), a selective lysosomal mechanism for degradation of cytosolic proteins. Pathogenic mutants of alpha-syn block lysosomal translocation, impairing their own degradation along with that of other CMA substrates. While pathogenic alpha-syn mutations are rare, alpha-syn undergoes posttranslational modifications, which may underlie its accumulation in cytosolic aggregates in most forms of PD. Using mouse ventral medial neuron cultures, SH-SY5Y cells in culture, and isolated mouse lysosomes, we have found that most of these posttranslational modifications of alpha-syn impair degradation of this protein by CMA but do not affect degradation of other substrates. Dopamine-modified alpha-syn, however, is not only poorly degraded by CMA but also blocks degradation of other substrates by this pathway. As blockage of CMA increases cellular vulnerability to stressors, we propose that dopamine-induced autophagic inhibition could explain the selective degeneration of PD dopaminergic neurons.
Figures


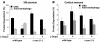

References
-
- Volles M., Lansbury P.J. Zeroing in on the pathogenic form of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism of neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease. Biochemistry. 2003;42:7871–7878. - PubMed
-
- Abeliovich A., et al. Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron. 2000;25:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Nussbaum R.L., Polymeropoulos M.H. Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997;6:1687–1691. - PubMed
-
- Lee V.M., Trojanowski J.Q. Mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease linked to pathological alpha-synuclein: new targets for drug discovery. Neuron. 2006;52:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

