Structural and functional studies of a family of Dictyostelium discoideum developmentally regulated, prestalk genes coding for small proteins
- PMID: 18173832
- PMCID: PMC2257962
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-1
Structural and functional studies of a family of Dictyostelium discoideum developmentally regulated, prestalk genes coding for small proteins
Abstract
Background: The social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum executes a multicellular development program upon starvation. This morphogenetic process requires the differential regulation of a large number of genes and is coordinated by extracellular signals. The MADS-box transcription factor SrfA is required for several stages of development, including slug migration and spore terminal differentiation.
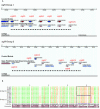
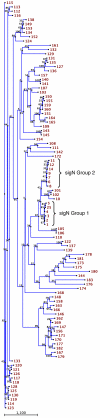
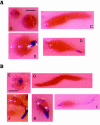
Results: Subtractive hybridization allowed the isolation of a gene, sigN (SrfA-induced gene N), that was dependent on the transcription factor SrfA for expression at the slug stage of development. Homology searches detected the existence of a large family of sigN-related genes in the Dictyostelium discoideum genome. The 13 most similar genes are grouped in two regions of chromosome 2 and have been named Group1 and Group2 sigN genes. The putative encoded proteins are 87-89 amino acids long. All these genes have a similar structure, composed of a first exon containing a 13 nucleotides long open reading frame and a second exon comprising the remaining of the putative coding region. The expression of these genes is induced at10 hours of development. Analyses of their promoter regions indicate that these genes are expressed in the prestalk region of developing structures. The addition of antibodies raised against SigN Group 2 proteins induced disintegration of multi-cellular structures at the mound stage of development.
Conclusion: A large family of genes coding for small proteins has been identified in D. discoideum. Two groups of very similar genes from this family have been shown to be specifically expressed in prestalk cells during development. Functional studies using antibodies raised against Group 2 SigN proteins indicate that these genes could play a role during multicellular development.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

