Inhibitory role of Plk1 in the regulation of p73-dependent apoptosis through physical interaction and phosphorylation
- PMID: 18174154
- PMCID: PMC2417181
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M710608200
Inhibitory role of Plk1 in the regulation of p73-dependent apoptosis through physical interaction and phosphorylation
Abstract
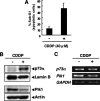
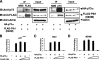
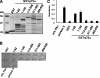
In response to DNA damage, p73 plays a critical role in cell fate determination. In this study, we have found that Plk1 (polo-like kinase 1) associates with p73, phosphorylates p73 at Thr-27, and thereby inhibits its pro-apoptotic activity. During cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in COS7 cells in which the endogenous p53 is inactivated by SV40 large T antigen, p73 was induced to accumulate in association with a significant down-regulation of Plk1. Consistent with these observations, Plk1 reduced the stability of the endogenous p73. Immunoprecipitation and in vitro pulldown assay demonstrated that p73 binds to the kinase domain of Plk1 through its NH(2)-terminal region. Luciferase reporter assay and reverse transcription-PCR analysis revealed that Plk1 is able to block the p73-mediated transcriptional activation. Of note, kinase-deficient Plk1 mutant (Plk1(K82M)) retained an ability to interact with p73; however, it failed to inactivate the p73-mediated transcriptional activation, suggesting that kinase activity of Plk1 is required for the inhibition of p73. Indeed, in vitro kinase assay indicated that p73 is phosphorylated at Thr-27 by Plk1. Furthermore, small interference RNA-mediated knockdown of the endogenous Plk1 in p53-deficient H1299 cells resulted in a significant increase in the number of cells with sub-G(1) DNA content accompanied by the up-regulation of p73 and pro-apoptotic p53(AIP1) as well as the proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Thus, our present results suggest that Plk1-mediated dysfunction of p73 is one of the novel molecular mechanisms to inhibit the p53-independent apoptosis, and the inhibition of Plk1 might provide an attractive therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment.
Figures



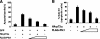



Similar articles
-
Plk3 inhibits pro-apoptotic activity of p73 through physical interaction and phosphorylation.Genes Cells. 2009 Jul;14(7):775-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2009.01309.x. Epub 2009 May 28. Genes Cells. 2009. PMID: 19490146
-
p73-mediated transcriptional activity is negatively regulated by polo-like kinase 1.Cell Cycle. 2008 May 1;7(9):1214-23. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.9.5777. Epub 2008 Feb 15. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18418051
-
Long-term downregulation of Polo-like kinase 1 increases the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(WAF1/CIP1).Cell Cycle. 2009 Feb 1;8(3):460-72. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.3.7651. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19177004
-
p73 tumor suppressor protein: a close relative of p53 not only in structure but also in anti-cancer approach?Cell Cycle. 2010 Feb 15;9(4):720-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.4.10668. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20160513 Review.
-
Battle of the eternal rivals: restoring functional p53 and inhibiting Polo-like kinase 1 as cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2013 Jul;4(7):958-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1096. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 23948487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PLK1 inhibition enhances temozolomide efficacy in IDH1 mutant gliomas.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):15827-15837. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15015. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28178660 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory functional territory of PLK-1 and their substrates beyond mitosis.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 6;8(23):37942-37962. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16290. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CK2 phosphorylates and inhibits TAp73 tumor suppressor function to promote expression of cancer stem cell genes and phenotype in head and neck cancer.Neoplasia. 2014 Oct 23;16(10):789-800. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.08.014. eCollection 2014 Oct. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25379016 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Post-Translational Modifications of the p73 Protein: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 15;13(8):1916. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081916. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor suppressor KIF1Bβ regulates mitochondrial apoptosis in collaboration with YME1L1.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Jul;58(7):1134-1144. doi: 10.1002/mc.22997. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 30859632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaghad, M., Bonnet, H., Yang, A., Creancier, L., Biscan, J. C., Valent, A., Minty, A., Chalon, P., Lelias, J. M., Dumont, X., Ferrara, P., McKeon, F., and Caput, D. (1997) Cell 90 809-819 - PubMed
-
- Melino, G., De Laurenzi, V., and Vousden, K. H. (2002) Nat. Rev. Cancer 2 605-615 - PubMed
-
- Stiewe, T., Zimmermann, S., Frilling, A., Esche, H., and Putzer, B. M. (2002) Cancer Res. 62 3598-3602 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

