Homeostatic regulation of AMPA receptor expression at single hippocampal synapses
- PMID: 18174334
- PMCID: PMC2206612
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706447105
Homeostatic regulation of AMPA receptor expression at single hippocampal synapses
Erratum in
-
Correction for Hou et al., Homeostatic regulation of AMPA receptor expression at single hippocampal synapses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 28;114(13):E2799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1702629114. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28265053 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
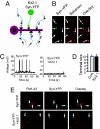
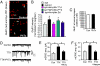
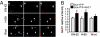
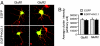
Homeostatic synaptic response is an important measure in confining neuronal activity within a narrow physiological range. Whether or not homeostatic plasticity demonstrates synapse specificity, a key feature characteristic of Hebbian-type plasticity, is largely unknown. Here, we report that in cultured hippocampal neurons, alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-isoxazole-4-propionic acid subtype glutamate receptor (AMPAR) accumulation is increased selectively in chronically inhibited single synapses, whereas the neighboring normal synapses remain unaffected. This synapse-specific homeostatic regulation depends on the disparity of synaptic activity and is mediated by GluR2-lacking AMPARs and PI3-kinase signaling. These results demonstrate the existence of synaptic specificity and the crucial role of AMPAR-gated calcium in homeostatic plasticity in central neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

