At the tipping point: accomplishing population-wide sodium reduction in the United States
- PMID: 18174765
- PMCID: PMC8109913
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2007.07227.x
At the tipping point: accomplishing population-wide sodium reduction in the United States
Figures

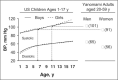
References
-
- He FJ, MacGregor GA. Effect of modest salt reduction on blood pressure: A meta‐analysis of randomized trials. implications for public health. J Hum Hypertens. 2002;16:761–770. - PubMed
-
- Johnson AG, Nguyen TV, Davis D. Blood pressure is linked to salt intake and modulated by the angiotensinogen gene in normotensive and hypertensive elderly subjects. J Hypertens. 2001;19:1053–1060. - PubMed
-
- Sacks FM, Svetkey LP, Vollmer WM, et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) diet. DASH‐sodium collaborative research group . N Engl J Med. 2001;344:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger MH, Miller JZ, Luft FC, et al. Definitions and characteristics of sodium sensitivity and blood pressure resistance. Hypertension. 1986;8:II127–II134. - PubMed
-
- Obarzanek E, Proschan MA, Vollmer WM, et al. Individual blood pressure responses to changes in salt intake: Results from the DASH‐sodium trial. Hypertension. 2003;42:459–467. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

