Perception of dynamic changes in facial affect and identity in autism
- PMID: 18174910
- PMCID: PMC2174259
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsm010
Perception of dynamic changes in facial affect and identity in autism
Abstract
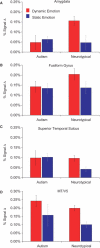
Despite elegant behavioral descriptions of abnormalities for processing emotional facial expressions and biological motion in autism, identification of the neural mechanisms underlying these abnormalities remains a critical and largely unmet challenge. We compared brain activity with dynamic and static facial expressions in participants with and without high-functioning autism using event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and three classes of face stimuli-emotion morphs (fearful and angry), identity morphs and static images (fearful, angry and neutral). We observed reduced activity in the amygdala (AMY) and fusiform gyrus (FFG) to dynamic emotional expressions in people with autism. There was also a lack of modulation by dynamic compared with static emotional expressions of social brain regions including the AMY, posterior superior temporal sulcus (STS) region and FFG. We observed equivalent emotion and identity morph-evoked activity in participants with and without autism in a region corresponding to the expected location of the more generally motion-sensitive area MT or V5. We conclude that dysfunctions in key components of the human face processing system including the AMY, FFG and posterior STS region are present in individuals with high-functioning autism, and this dysfunction might contribute to the deficits in processing emotional facial expressions.
Keywords: amygdala; autism; emotion; fMRI; face processing.
Figures

References
-
- Adolphs R, Gosselin F, Buchanan TW, Tranel D, Schyns P, Damasio AR. A mechanism for impaired fear recognition after amygdala damage. Nature. 2005;433:68–72. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Sears L, Piven J. Abnormal processing of social information from faces in autism. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2001;13:232–40. - PubMed
-
- Ashwin C, Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, O'Riordan M, Bullmore ET. Differential activation of the amygdala and the ‘social brain’ during fearful face-processing in Asperger Syndrome. Neuropsychologia. 2007;45:2–14. - PubMed
-
- Association AP. American Psychiatric Association; 2000. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV-TR.
-
- Baron-Cohen S, Ring HA, Wheelwright S, et al. Social intelligence in the normal and autistic brain: an fMRI study. European Journal of Neuroscience. 1999;11:1891–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

