Steroid receptor coactivator 2 is required for female fertility and mammary morphogenesis: insights from the mouse, relevance to the human
- PMID: 18174919
- PMCID: PMC2121321
- DOI: 10.1621/nrs.05011
Steroid receptor coactivator 2 is required for female fertility and mammary morphogenesis: insights from the mouse, relevance to the human
Abstract
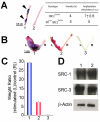
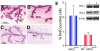
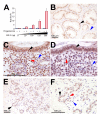
Although the importance of the progesterone receptor (PR) to female reproductive and mammary gland biology is firmly established, the coregulators selectively co-opted by PR in these systems have not been clearly delineated. A selective gene-knockout approach applied to the mouse, which abrogates gene function only in cell types that express PR, recently disclosed steroid receptor coactivator 2 (SRC-2, also known as TIF-2 or GRIP-1) to be an indispensable coregulator for uterine and mammary gland responses that require progesterone. Uterine cells positive for PR (but devoid of SRC-2) were found to be incapable of facilitating embryo implantation, a necessary first step toward the establishment of the materno-fetal interface. Importantly, such an implantation defect is not exhibited by knockouts for SRC-1 or SRC-3, underscoring the unique coregulator importance of SRC-2 in peri-implantation biology. Moreover, despite normal levels of PR, SRC-1 and SRC-3, progesterone-dependent branching morphogenesis and alveologenesis fails to occur in the murine mammary gland in the absence of SRC-2, thereby establishing a critical coregulator role for SRC-2 in signaling cascades that mediate progesterone-induced mammary epithelial proliferation. Finally, the recent detection of SRC-2 in the human endometrium and breast suggests that this coregulator may represent a new clinical target for the future management of female reproductive health and/or breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Anzick S. L., Kononen J., Walker R. L., Azorsa D. O., Tanner M. M., Guan X. Y., Sauter G., Kallioniemi O. P., Trent J. M., Meltzer P. S. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1997;277:965–8. - PubMed
-
- Belandia B., Parker M. G. Functional interaction between the p160 coactivator proteins and the transcriptional enhancer factor family of transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:30801–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

